Traffic Control
Dubbo provides rich traffic control strategies
- Address Discovery and Load Balancing: Address discovery supports dynamic online and offline service instances, and load balancing ensures that traffic is evenly distributed to each instance.
- Traffic Control Based on Routing Rules: Routing rules perform conditional matching for each request and route requests that meet the conditions to a specific subset of addresses.
Service discovery ensures that the caller sees the latest provider instance addresses. The service discovery mechanism relies on the registry (Zookeeper, Nacos, Istio, etc.). On the consumer side, Dubbo provides various load balancing strategies, such as random load balancing, consistent hash load balancing, weight-based round-robin, least active priority, P2C, etc.
Dubbo’s traffic control rules can precisely control traffic direction based on the granularity of applications, services, methods, parameters, etc. They match the target service, method, and other additional parameters in the request body. Traffic that meets the matching conditions will be further forwarded to a subset of addresses according to specific rules. The traffic control rules include:
- Conditional Routing Rules
- Tag Routing Rules
- Script Routing Rules
- Dynamic Configuration Rules
If the underlying RPC protocol is based on HTTP (such as REST, gRPC, Triple, etc.), then services and methods are uniformly mapped to HTTP paths. In this case, Dubbo routing rules are equivalent to traffic distribution mechanisms based on HTTP paths and headers.
In Dubbo, there are concepts of applications, services, and methods. An application can publish multiple services, and a service contains multiple callable methods. From an abstract perspective, a Dubbo call is an invocation of a specific method of a service within a provider application initiated by a consumer application. Dubbo’s traffic control rules can precisely control traffic direction based on the granularity of applications, services, methods, parameters, etc.
Working Principle
The following is the working process of a single router in Dubbo. The router receives a set of instance addresses of a service as input, matches the input addresses based on the request context and the actual routing rule definitions. All successfully matched instances form a subset of addresses, and the final subset of addresses is handed over to the next router or load balancing component for processing.
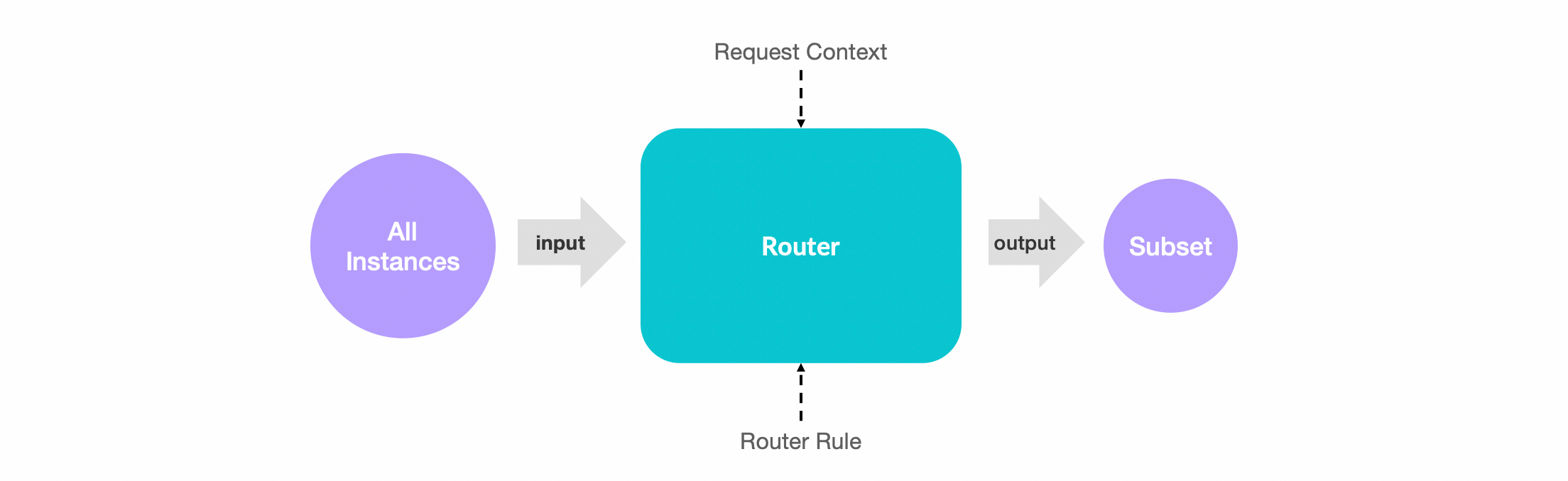
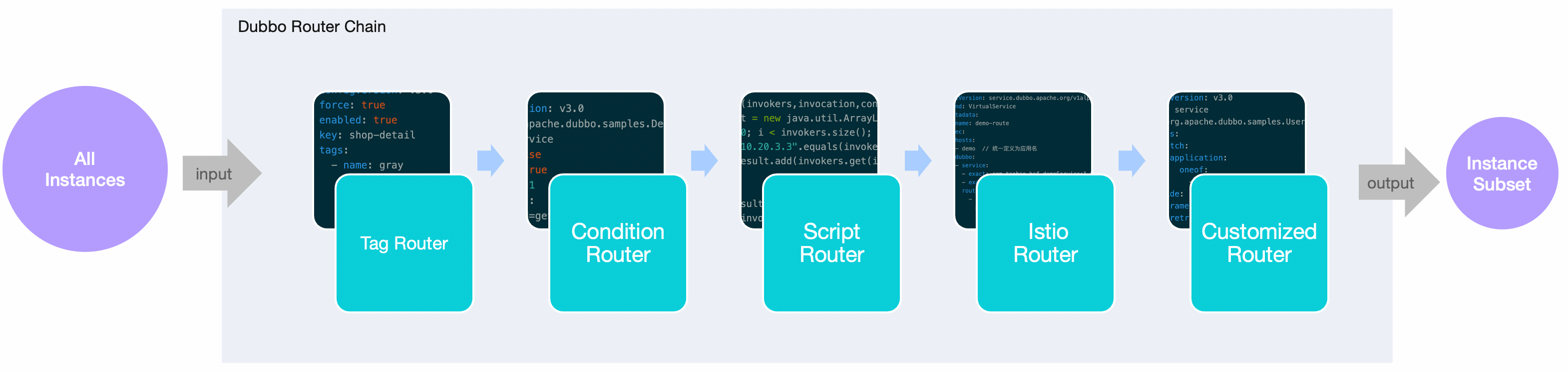
Typically, in Dubbo, multiple routers form a routing chain that works together. The output of the previous router serves as the input for another router. After layer-by-layer routing rule filtering, an effective address set is finally generated.
- Each service in Dubbo has a completely independent routing chain. The composition of the routing chain for each service may differ, and the rules processed vary, with no mutual influence between services.
- For a single routing chain, even if the input address set is the same each time, the resulting subset of addresses may differ based on the different request contexts each time.
Classification of Routing Rules
Tag Routing Rules
Tag routing divides instances of a service into different groups, constraining traffic with specific tags to flow only within designated groups. Different groups serve different traffic scenarios, achieving traffic isolation. Tag routing can serve as the foundation for scenarios like blue-green deployment and grayscale release.
Tag routing rules are an either-or traffic isolation solution, meaning requests that match the tag will be 100% forwarded to instances with the same tag, and requests that do not match the tag will be 100% forwarded to the remaining unmatched instances. If you need a proportional traffic scheduling solution, please refer to the example Proportional Traffic Routing Based on Weight.
Tags mainly refer to the grouping of provider application instances. Currently, there are two ways to complete instance grouping: dynamic rule tagging and static rule tagging. Dynamic rule tagging can dynamically enclose a group of machine instances at runtime, while static rule tagging requires instance restart to take effect. Among them, dynamic rules have higher priority than static rules, and when both rules exist and conflict, dynamic rules will prevail.
Tag Rule Example - Static Tagging
Static tagging needs to be determined before the service provider instance starts and must be specified through a specific parameter tag.
Provider
Before the Dubbo instance starts, specify the tag for the current instance, such as specifying tag=gray for instances deployed in the Hangzhou region.
<dubbo:provider tag="gray"/>
or
<dubbo:service tag="gray"/>
or
java -jar xxx-provider.jar -Ddubbo.provider.tag=gray
Consumer
The party initiating the call sets the traffic tag via tag before each request to ensure that the traffic is routed to the service provider with the same tag.
RpcContext.getContext().setAttachment(Constants.TAG_KEY, "gray");
Tag Rule Example - Dynamic Tagging
Compared to static tagging, which can only be set via the tag attribute and is fixed at startup, dynamic tags can match any number of attributes and dynamically divide Provider instances into different traffic groups based on specified matching conditions.
Provider
The following rule dynamically groups the shop-detail application, with instances matching env: gray being grouped into the gray group, while others that do not match env: gray remain in the default group (no tag).
configVersion: v3.0
force: true
enabled: true
key: shop-detail
tags:
- name: gray
match:
- key: env
value:
exact: gray
This involves how to label your instances with various raw labels, such as
envin the example above. One way is to write it directly in the configuration file, as shown in the provider section of the static rule example above. Another way is to specify it through preset environment variables. For more details, please refer to the section How to Label Instances below.
Consumer
The settings for the service initiator are consistent with the previous static tagging rules. You only need to set the traffic tag via tag before each request to ensure that the traffic is routed to the service provider with the same tag.
RpcContext.getContext().setAttachment(Constants.TAG_KEY, "Hangzhou");
Traffic with the above tag will be routed to instances divided into the hangzhou-region.
The scope of the request tag is limited to a single point-to-point RPC request. For example, in an A -> B -> C call chain, if the A -> B call sets the
tagparameter viasetAttachment, this parameter will not be effective in the B -> C call. Similarly, after completing the entire A -> B -> C call and A receives the result, if you want the sametagparameter, you still need to setsetAttachmentseparately before initiating another call. You can refer to Example Task - Environment Isolation for more information on the full-link transmission solution oftag.
Conditional Routing Rules
Conditional routing works similarly to tag routing, where the parameters in the request are matched first, and requests that meet the matching conditions are forwarded to a subset of specific instance addresses. Compared to tag routing, conditional routing is more flexible in its matching method:
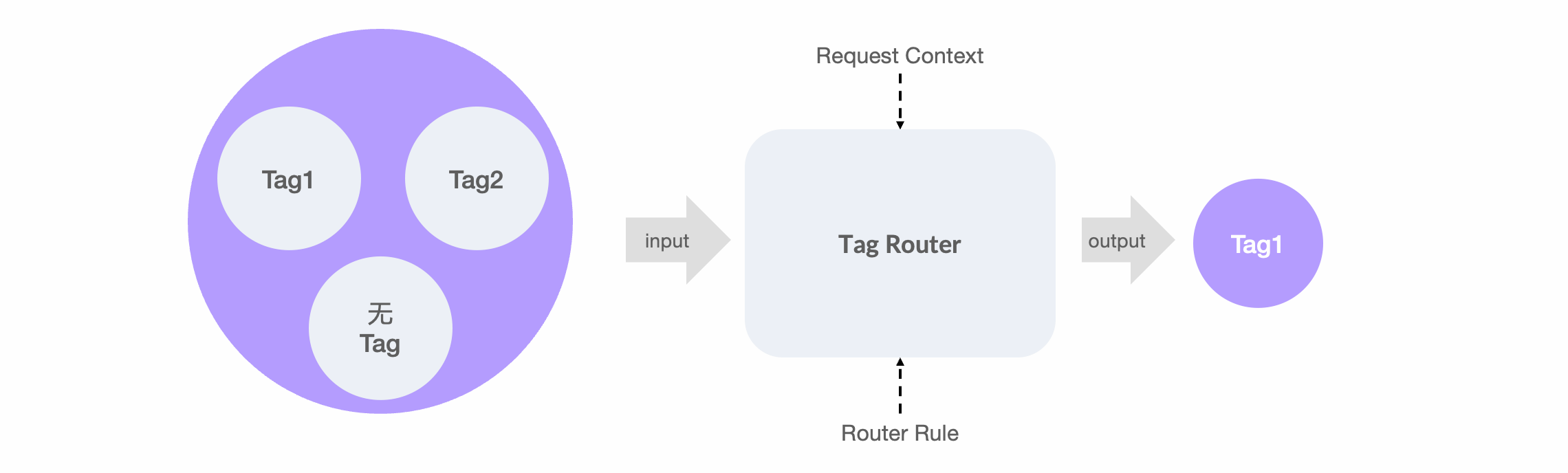
- In tag routing, once a tag is assigned to one or more machine instances, those instances are immediately removed from the general traffic pool, and there is no overlap between different tags. It’s somewhat like the diagram below, where the address set is clearly divided at the input stage.
- From the perspective of conditional routing, all instances are consistent, and there is no grouping isolation during the routing process. Each routing filter is executed based on the full address set.
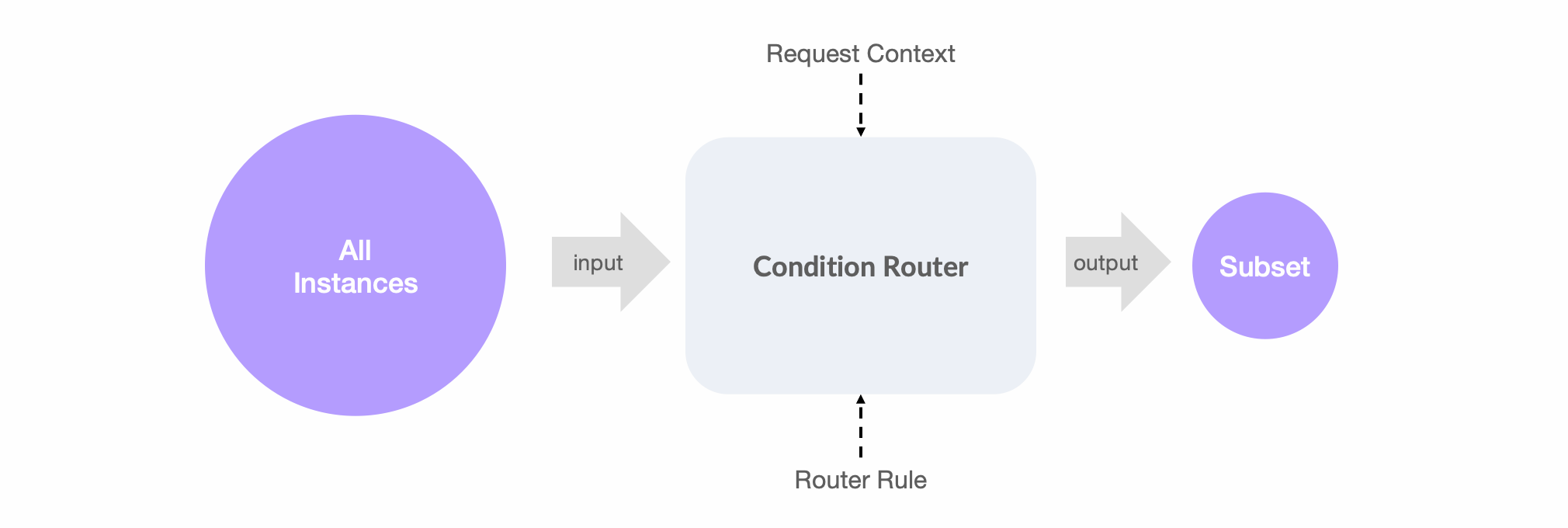
The main content of the conditional routing rule conditions includes two parts:
- The part before
=>is the request parameter matching condition. Thematching condition specified parameterwill be compared with theconsumer's request context (URL) or even method parameters. When the consumer meets the matching condition, the address subset filtering rule after=>will be executed for that consumer. - The part after
=>is the address subset filtering condition. Thefiltering condition specified parameterwill be compared with theprovider instance address (URL). The consumer will ultimately get a list of instances that meet the filtering conditions, ensuring that traffic is only sent to the address subset that meets the conditions.- If the matching condition is empty, it applies to all requests, such as:
=> status != staging - If the filtering condition is empty, it means access from the corresponding request is prohibited, such as:
application = product =>
- If the matching condition is empty, it applies to all requests, such as:
Conditional Routing Rule Example
Based on the following example rule, all org.apache.dubbo.demo.CommentService service calls will be forwarded to the address subset with the same region tag as the current consumer machine. $region is a special reference symbol that will be replaced with the actual region value of the consumer machine during execution.
configVersion: v3.0
enabled: true
force: false
key: org.apache.dubbo.samples.CommentService
conditions:
- '=> region = $region'
For conditional routing, we usually recommend configuring rules with
scope: servicebecause it can take effect across consumer applications for all applications consuming a specific service. For more information onscopeandservice,applicationin Dubbo rules, please read the Conditional Routing Rule Manual.
Conditional routing rules also support setting specific machine addresses such as IP or port. In this case, conditional routing can handle some temporary situations for development or online machines, achieving operational effects such as blacklist, whitelist, temporary removal of instances, etc. For example, the following rule can exclude the machine 172.22.3.91 from the available list of services.
=> host != 172.22.3.91
Conditional routing also supports matching based on request parameters, as shown in the following example:
conditions:
- method=getDetail&arguments[0]=dubbo => port=20880
Dynamic Configuration Rules
Through the dynamic configuration rules provided by Dubbo, you can dynamically modify the runtime behavior of Dubbo service processes without restarting, and the configuration parameters take effect in real-time. Based on this powerful feature, almost all runtime parameters can be dynamically adjusted, such as timeout settings, temporarily enabling Access Log, modifying Tracing sampling rate, adjusting rate limiting and degradation parameters, load balancing, thread pool configuration, log levels, dynamically tagging machine instances, etc. Similar to the traffic control rules mentioned above, dynamic configuration rules support two granularities: application and service, meaning you can choose to adjust the parameter configuration of only one or several services in the application at a time.
Of course, for the sake of system stability and security, some specific parameters are not allowed to be dynamically modified. But other than that, almost all parameters can be dynamically modified, and many powerful runtime capabilities can be achieved through this rule. You can try it out with a sample application. Usually, the parameters in the URL address can be modified, which is also recorded in more detail in the reference manuals for each language implementation.
Dynamic Configuration Rule Example - Modify Timeout
The following example adjusts the timeout parameter of the org.apache.dubbo.samples.UserService service to 2000ms
configVersion: v3.0
scope: service
key: org.apache.dubbo.samples.UserService
enabled: true
configs:
- side: provider
parameters:
timeout: 2000
The following section specifies that this configuration is at the service granularity, and the specific service name to be changed is org.apache.dubbo.samples.UserService. scope supports two optional values: service and application. If scope: service, then key should be configured in the format version/service:group.
scope: service
key: org.apache.dubbo.samples.UserService
For more information on
scopeandservice,applicationin Dubbo rules, please refer to the Dynamic Configuration Reference Manual or Dynamic Configuration Example.
The parameters parameter specifies the new modification value, here setting the timeout to 2000ms through timeout: 2000.
parameters:
timeout: 2000
Script Routing Rules
Script routing is the most intuitive routing method, and it is also the most flexible routing rule currently because you can define any address filtering rules in the script. If we define a script rule for a service, all subsequent requests will first execute this script, and the addresses filtered out by the script will be the set of valid addresses to which the request is allowed to be sent.
configVersion: v3.0
key: demo-provider
type: javascript
enabled: true
script: |
(function route(invokers,invocation,context) {
var result = new java.util.ArrayList(invokers.size());
for (i = 0; i < invokers.size(); i ++) {
if ("10.20.3.3".equals(invokers.get(i).getUrl().getHost())) {
result.add(invokers.get(i));
}
}
return result;
} (invokers, invocation, context));
How to Tag Instances
Currently, there are two ways to specify tags for Dubbo instances at the startup stage. One is the method mentioned earlier, configuring within the application, such as setting <dubbo:provider tag="gray"/> in the XML file. The application will be automatically tagged after packaging and deployment.
Another more flexible way is to tag the application by reading the environment information on the deployed machine. This way, the application’s tags can dynamically and automatically populate with the instance, avoiding the need to repackage the application image every time the deployment environment changes. Currently, Dubbo can automatically read the following environment variable configurations:
spec:
containers:
- name: detail
image: apache/demo-detail:latest
env:
- name: DUBBO_LABELS
value: "region=hangzhou; env=gray"
spec:
containers:
- name: detail
image: apache/demo-detail:latest
env:
- name: DUBBO_ENV_KEYS
value: "REGION, ENV"
- name: REGION
value: "hangzhou"
- name: ENV
value: "gray"
If you have a different instance environment storage mechanism, you can customize your own tag loading method by extending the InfraAdapter extension point. If your application is deployed in a Kubernetes environment and has integrated with the service mesh system, you can also use the standard deployment tag method for tagging. For details, please follow the Service Mesh Task Example.
How to Configure Traffic Rules
Dubbo provides a console called Dubbo Admin to help you visualize and issue traffic control rules, and monitor the effectiveness of the rules in real-time.
Dubbo also provides the dubboctl command-line tool, which requires Dubbo Admin to be pre-deployed and ready, as dubboctl issues rules through HTTP communication with Admin.
If you are using a service mesh architecture like Istio, you can also use Istioctl, kubectl, etc., to issue Istio standard rules.
Integrating with Service Mesh
The above introduces traffic governance rules within the Dubbo system. If you are interested in service mesh architecture, you can integrate Dubbo services into the service mesh system. This way, you can use the traffic governance capabilities provided by the service mesh, such as Istio’s VirtualService.
For details, please refer to Service Mesh Architecture in Dubbo.
Learn by Example
We have set up an online shopping system for you to learn the specific usage of traffic rules.