Version and Group
In Dubbo services, an interface cannot uniquely identify a service. Only the tuple interface + group + version can uniquely identify a service.
- When the same interface is used for different business scenarios, usage needs, or functional modules, service groups can be used to distinguish different implementations. At the same time, these different implementations can coexist and call each other.
- When the interface implementation needs upgrading while retaining the original implementation, we can distinguish them using different version numbers.
The complete source code of this article’s examples can be found at the following links:
Usage
Using the @DubboService annotation, configure the group and version parameters:
Interface definition:
public interface DevelopService {
String invoke(String param);
}
Implementation 1:
@DubboService(group = "group1", version = "1.0")
public class DevelopProviderServiceV1 implements DevelopService{
@Override
public String invoke(String param) {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append("ServiceV1 param:").append(param);
return s.toString();
}
}
Implementation 2:
@DubboService(group = "group2", version = "2.0")
public class DevelopProviderServiceV2 implements DevelopService{
@Override
public String invoke(String param) {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append("ServiceV2 param:").append(param);
return s.toString();
}
}
Client Interface Call:
Use the @DubboReference annotation, adding the group and version parameters
@DubboReference(group = "group1", version = "1.0")
private DevelopService developService;
@DubboReference(group = "group2", version = "2.0")
private DevelopService developServiceV2;
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
// Call the DevelopService implementation in group1
System.out.println("Dubbo Remote Return ======> " + developService.invoke("1"));
// Call another implementation of DevelopService
System.out.println("Dubbo Remote Return ======> " + developServiceV2.invoke("2"));
}
Service Consumer Side (Annotation Configuration)
Using the @DubboReference annotation, add the group parameter
@DubboReference(group = "demo")
private DemoService demoService;
@DubboReference(group = "demo2")
private DemoService demoService2;
// the group value is *, indicating matching any service group
@DubboReference(group = "*")
private DemoService demoService3;
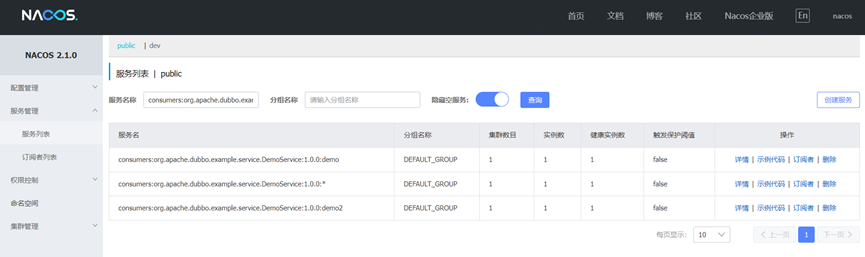
After starting the Dubbo service, the same service name with different groups can be seen in the registry, for example using Nacos as the registry:
Service Provider Side (XML Configuration)
Using the <dubbo:service /> tag, add the group parameter
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo
http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
...
<dubbo:service interface="org.apache.dubbo.example.service.DemoService" group="demo"/>
<dubbo:service interface="org.apache.dubbo.example.service.DemoService" group="demo2"/>
...
</beans>
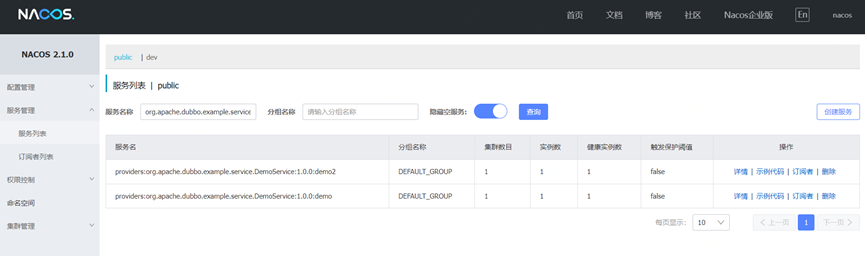
After starting the Dubbo service, the same service name with different groups can be seen in the registry:
Service Consumer Side (XML Configuration)
Using the dubbo:reference/ annotation, add the group parameter
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd
http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo
http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
...
<!-- Reference service interface -->
<dubbo:reference id="demoService" interface="org.apache.dubbo.example.service.DemoService" group="demo"/>
<dubbo:reference id="demoService2" interface="org.apache.dubbo.example.service.DemoService" group="demo2"/>
<!-- group value is *, indicating matching any service group -->
<dubbo:reference id="demoService3" interface="org.apache.dubbo.example.service.DemoService" group="*"/>
...
</beans>
After starting the Dubbo service, the same service name with different groups can be seen in the registry:

Service Provider Side (API Configuration)
Using the org.apache.dubbo.config.ServiceConfig class, add the group parameter
// ServiceConfig is a heavy object, encapsulating the connection with the registry and starting the server port
// Please cache it yourself to avoid memory and connection leaks
ServiceConfig<DemoService> service = new ServiceConfig<>();
service.setInterface(DemoService.class);
service.setGroup("demo");
...
ServiceConfig<DemoService> service2 = new ServiceConfig<>();
service2.setInterface(DemoService.class);
service2.setGroup("demo2");
...
After starting the Dubbo service, the same service name with different groups can be seen in the registry:

Service Consumer Side (API Configuration)
Using org.apache.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig, add the group parameter
// ReferenceConfig is a heavy object, encapsulating the connection with the registry and starting the server port
// Please cache it yourself to avoid memory and connection leaks
ReferenceConfig<DemoService> reference = new ReferenceConfig<>();
reference.setInterface(DemoService.class);
reference.setGroup("demo");
...
ReferenceConfig<DemoService> reference2 = new ReferenceConfig<>();
reference2.setInterface(DemoService.class);
reference2.setGroup("demo2");
...
ReferenceConfig<DemoService> reference3 = new ReferenceConfig<>();
reference3.setInterface(DemoService.class);
reference3.setGroup("*");
...
After starting the Dubbo service, the same service name with different groups can be seen in the registry:

Always only call one available group’s implementation
Group Aggregation
Aggregate results by group and return the aggregated result. For example, in a menu service, using group to distinguish various implementations of the same interface, the consumer needs to call once from each group and return results, merging them afterward.
The relevant code can refer to the example in the dubbo project.
Access multiple service providers as one provider. Applications can access multiple services as if they were accessing one service, allowing for more efficient resource use.
Search All Groups
<dubbo:reference interface="com.xxx.MenuService" group="*" merger="true" />
Merge Specified Groups
<dubbo:reference interface="com.xxx.MenuService" group="aaa,bbb" merger="true" />
Merge Specified Method
Specify to merge the results for a particular method; other unspecified methods will only call one Group.
<dubbo:reference interface="com.xxx.MenuService" group="*">
<dubbo:method name="getMenuItems" merger="true" />
</dubbo:reference>
Do Not Merge a Specific Method
Do not merge results for a specific method; others will merge.
<dubbo:reference interface="com.xxx.MenuService" group="*" merger="true">
<dubbo:method name="getMenuItems" merger="false" />
</dubbo:reference>
Specify Merge Strategy
Specify the merge strategy. By default, it matches automatically based on the return value type. If there are two merge methods of the same type, specify the name of the merger Merge Result Description.
<dubbo:reference interface="com.xxx.MenuService" group="*">
<dubbo:method name="getMenuItems" merger="mymerge" />
</dubbo:reference>
Specify Merge Method
Specify the merge method, calling a designated method on the returned result to perform the merging; the parameter type of the merge method must be the same as the return result type.
<dubbo:reference interface="com.xxx.MenuService" group="*">
<dubbo:method name="getMenuItems" merger=".addAll" />
</dubbo:reference>
Tip
Supported from2.1.0Cross-Version Upgrade
Follow these steps for version migration
- During low-pressure periods, first upgrade half of the providers to the new version.
- Then upgrade all consumers to the new version.
- Finally, upgrade the remaining half of the providers to the new version.
Configuration
- Old and new version service providers.
- Old and new version service consumers.
When an interface implementation faces an incompatible upgrade, version numbers can be used as a transition, ensuring that services with different version numbers do not reference each other.
Reference Case https://github.com/apache/dubbo-samples/tree/master/dubbo-samples-version
Service Provider
Configuration for old version service provider
<dubbo:service interface="com.foo.BarService" version="1.0.0" />
Configuration for new version service provider
<dubbo:service interface="com.foo.BarService" version="2.0.0" />
Service Consumer
Configuration for old version service consumer
<dubbo:reference id="barService" interface="com.foo.BarService" version="1.0.0" />
Configuration for new version service consumer
<dubbo:reference id="barService" interface="com.foo.BarService" version="2.0.0" />
Without Version Distinction
If version distinction is not required, you can configure it as follows:
<dubbo:reference id="barService" interface="com.foo.BarService" version="*" />