Proxyless Service Mesh
1. What is Proxyless Service-Mesh?
1.1 Brief Analysis of Service Mesh
Istio is the most popular open-source service mesh today. It consists of a control plane and a data plane, as shown in the architecture below, image sourced from istio official website
The control plane located at the bottom half of the image is responsible for the distribution of resources like configurations, service information, and certificates. The data plane, located at the upper half, focuses on the communication traffic between services; traditional service meshes intercept all business network traffic through proxies, which need to be aware of the configuration resources issued by the control plane to manage traffic directions as required.
In the Istiod environment, the control plane is a process called istiod, and the network proxy is envoy. Istiod obtains service information by listening to K8S resources such as Service, Endpoint, etc., and uniformly distributes these resources to the network proxy located in the data plane through the XDS protocol. Envoy runs as a sidecar alongside business application Pods, sharing the same host network and hijacking the application’s network traffic by modifying the routing table.
Service Mesh can solve numerous problems in microservices scenarios. As cluster scales increase and business complexity grows, native k8s-based container orchestration solutions become challenging, and developers face significant service governance challenges. Service Mesh effectively addresses this issue by encapsulating service governance needs in the control plane and proxies, allowing business developers to focus solely on business logic. After application deployment, operations personnel can utilize configuration changes to enable functionalities like fault recovery, load balancing, and gray release, significantly enhancing development and iteration efficiency.
Istio’s sidecar accompanies the entire lifecycle of business application processes through container injection, making it non-intrusive to the business application, which solves issues related to application portability, multi-language interoperability, and infrastructure coupling but also leads to high resource consumption and increased request latency.
Service provides a good approach to service governance by decoupling infrastructure from business logic, allowing application developers to focus solely on business matters. On the other hand, due to the drawbacks of sidecar, we can consider using an SDK to support the data plane.
1.2 Proxyless Service-Mesh
Proxyless Service Mesh is a new concept proposed in recent years, with open-source communities like Istio, gRPC, and brpc exploring and practicing in this direction. The proxyless service mesh framework is introduced into business applications in the form of SDKs, responsible for communication and governance between services. Configurations from the control plane are directly distributed to the service framework, which replaces the earlier role of the sidecar.
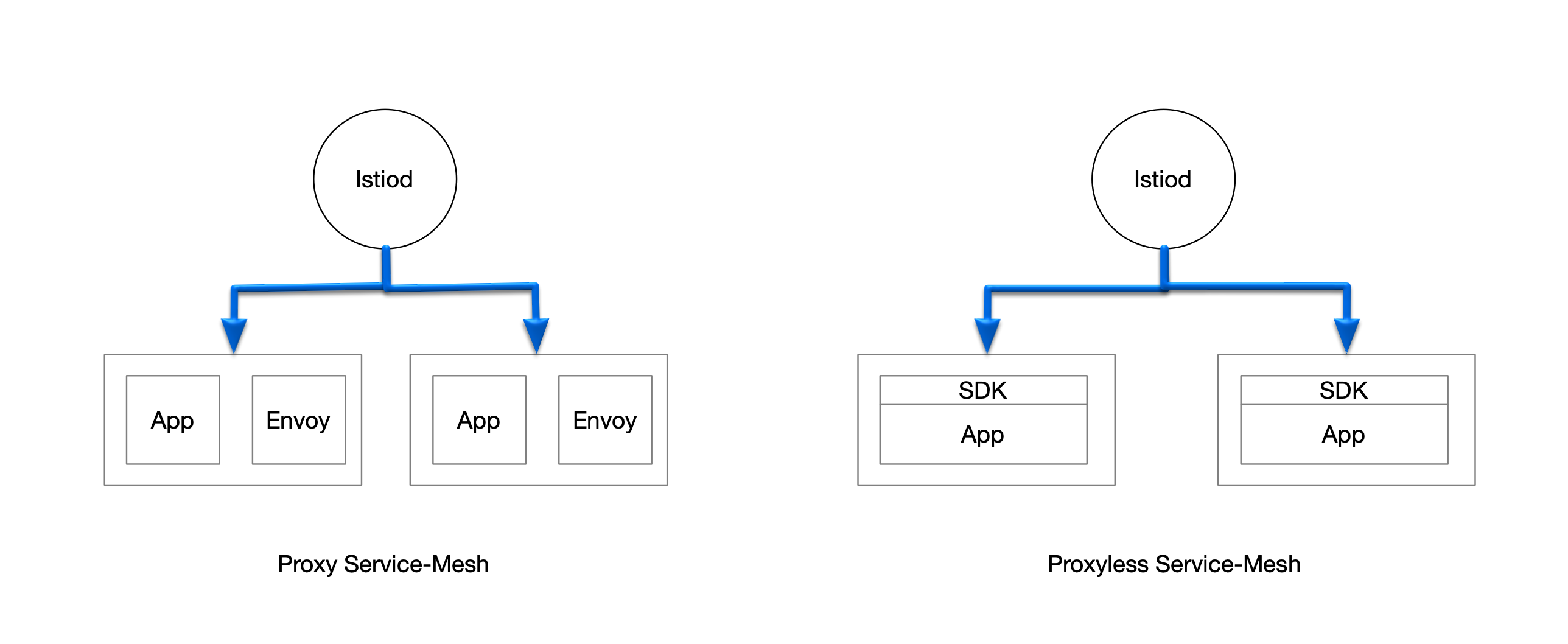
The main capabilities of the service framework (SDK) can be summarized as follows:
- Connect to the control plane and listen for configuration resources.
- Connect to applications and provide convenient interfaces for developers.
- Connect to the network and respond to traffic rules based on resource changes.
1.3 Advantages and Disadvantages of Proxyless
Advantages:
- Performance: Direct communication in the proxyless mode has much lower network latency compared to proxy mode.
- Stability: The proxyless mode operates as a single process, with a simple topology, making debugging easier and enhancing stability.
- Framework Integration: Many service frameworks with SDK patterns are already available in the market, allowing easy reuse of existing capabilities when switching to mesh.
- Resource Consumption: Without sidecar, resource usage is low.
Disadvantages:
- Language Binding: Multiple languages SDKs need to be developed.
- Low Portability: Infrastructure cannot be upgraded non-intrusively by switching sidecars.
Overall, the Proxyless architecture, with its high performance and stability, is more suitable for production environments.
2. Dubbo-go and Proxyless Service-Mesh
2.1 Design of Dubbo-go in Proxyless Service-Mesh Scenarios
Service Registration Discovery
Dubbo-go has extensible service registration and discovery capabilities, with an implementation fitting for service mesh scenarios. Developers can register dubbo-go application information on the Istiod control plane. Client applications can query the registered interface data for service discovery.
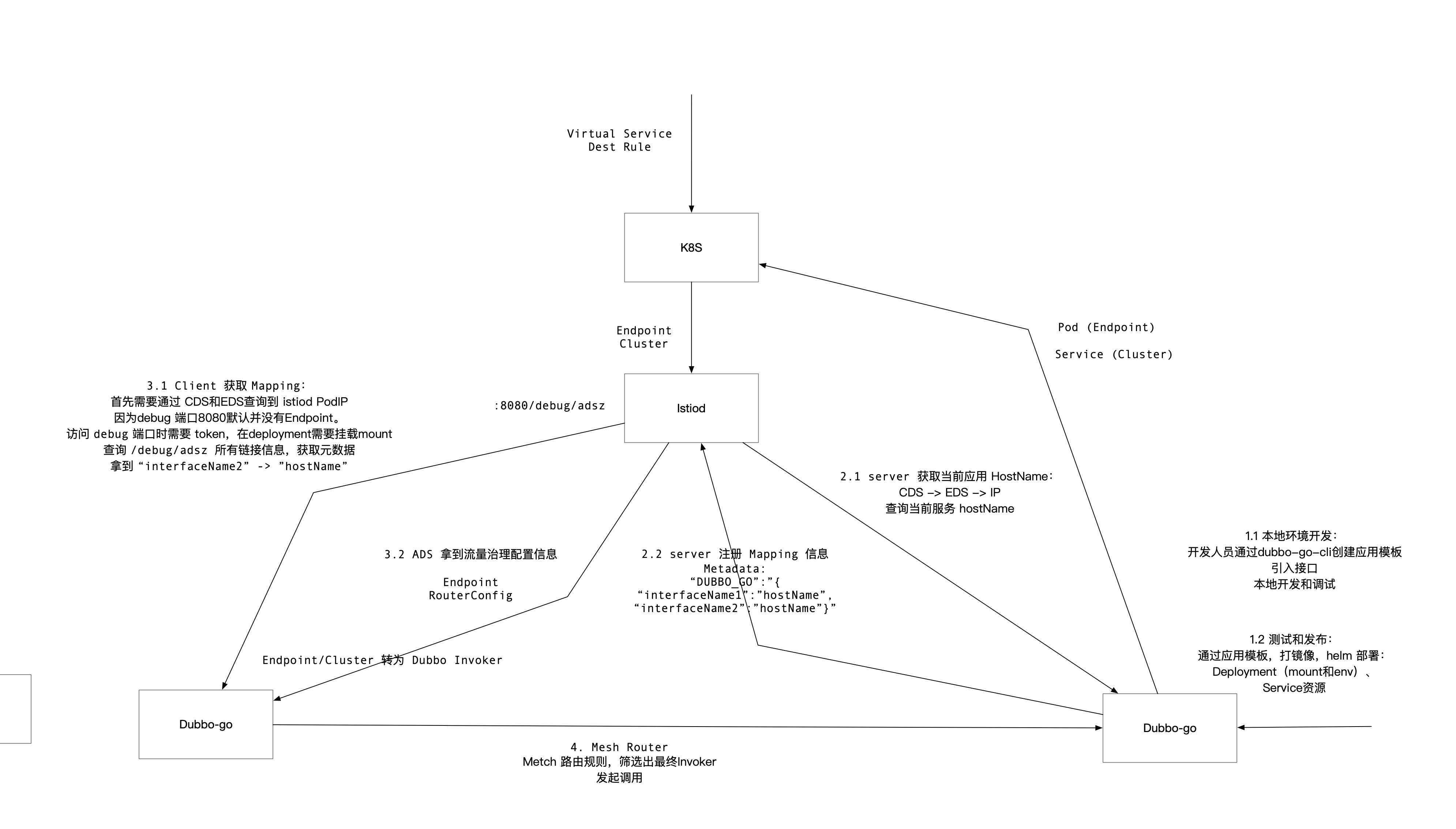
- Developers use the dubbogo-cli tool to create application templates and publish Deployments / Services to the cluster.
- The server pulls a complete CDS and EDS, compares the local IP, acquires the current application’s hostname, and registers the mapping of all interface names to hostnames in Istiod.
- The client pulls the complete mapping of interface names to hostnames from Istiod and caches it locally. When a call is made, it queries the local cache, converts the interface name to a hostname, and pulls the current cluster’s complete endpoints through CDS and EDS.
- The complete endpoints are filtered by the built-in Mesh Router of Dubbo-go, obtaining the final subset of endpoints and making requests based on the configured load balancing strategy.
Throughout the process, developers only need to focus on interfaces without worrying about hostname and port information. Both server-side developers only need to implement pb interfaces, exposing them through the framework; client-side developers only need to include pb interfaces and initiate calls directly.
Traffic Governance
Dubbo-go has routing capabilities; through the xds protocol, clients subscribe to routing configurations from Istiod and update local routing rules in real time to manage services. Dubbo-go is compatible with Istio’s traffic governance rules, allowing traffic routing to specified subsets through configurations of Virtual Services and Destination Rules, as well as deeper usage in scenarios like gray releases and traffic cuts.
Cloud-Native Scaffolding
dubbogo-cli is a sub-project of the Apache/dubbo-go ecosystem, providing developers with convenient functions like application template creation, tool installation, and interface debugging to enhance user development efficiency.
For details, please refer to 【dubbogo-cli tool】
3. Advantages of Dubbo-go-Mesh
3.1 Interface-Level Service Discovery
As mentioned earlier, the advantages of interface-level service registration and discovery mean that developers do not need to worry about downstream hostnames and port numbers; they only need to import interface stubs or implement interfaces to start using the framework.
3.2 High Performance
We deployed the Istio environment within the k8s cluster and tested gRPC service calls in sidecar mode against Dubbo-go application service calls in Proxyless mode. We found that Proxyless mode had an order of magnitude lower request duration than sidecar mode, yielding approximately a tenfold performance improvement.
3.3 Cross-Ecosystem
Dubbo-go is a service framework that spans multiple ecosystems.
Mesh Ecosystem
Developers can utilize Dubbo-go for application development while leveraging powerful capabilities offered by the Istio ecosystem.
gRPC Ecosystem
- Dubbo-go supports interoperability with gRPC services and HTTP2 protocol stack.
- Dubbo-go uses pb serialization by default for high performance.
Dubbo Ecosystem
- Multi-language advantages enable interoperability between go-java applications.
- Compatible with Pixiu gateway, facilitating service exposure and protocol conversion.
- Utilizes components from the Dubbo-go ecosystem.