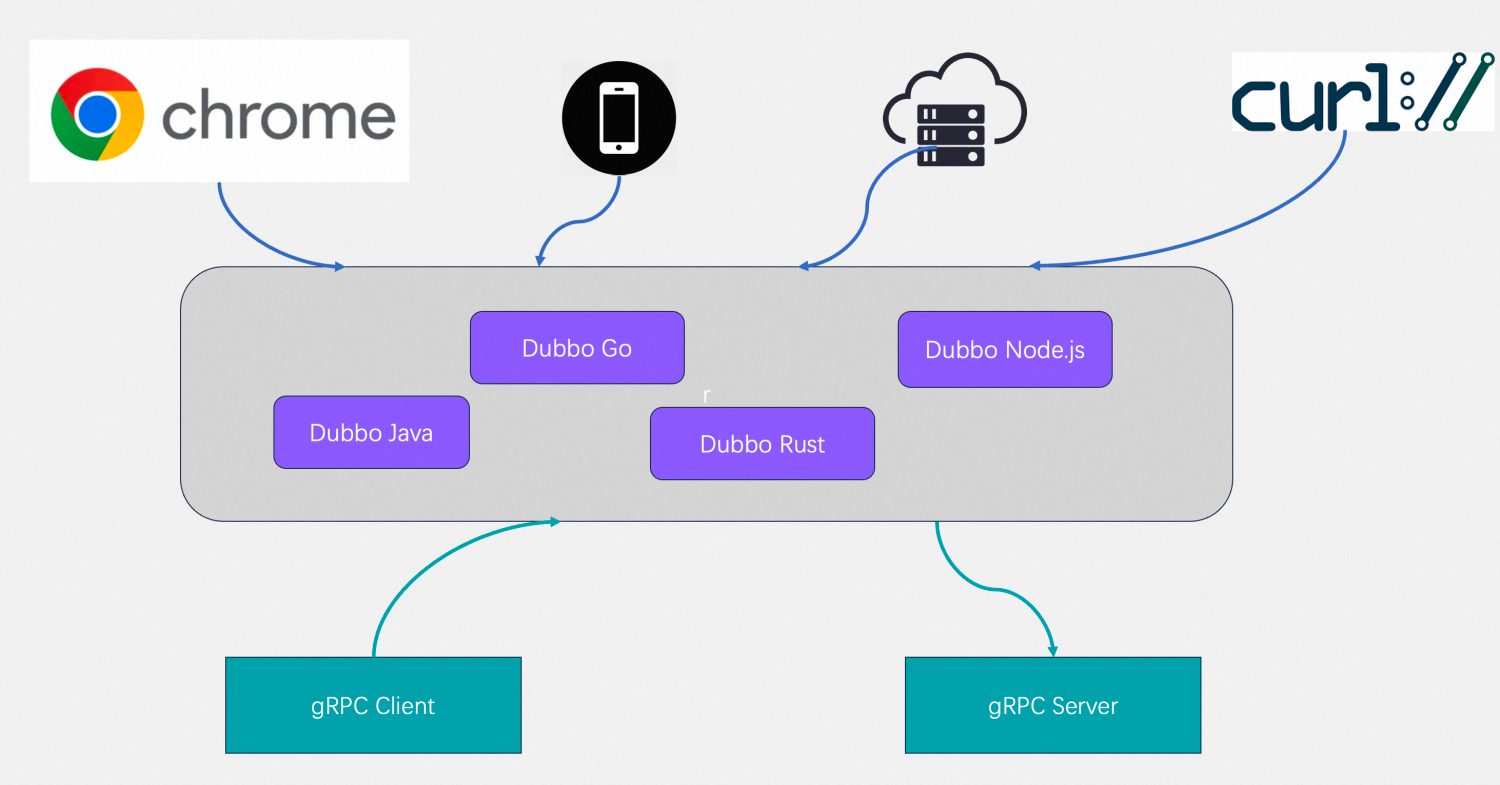
Can web browser pages access Dubbo and gRPC microservices? Dubbo-js alpha version officially released
Based on the Triple protocol defined by Dubbo3, you can easily write browser and gRPC-compatible RPC services, allowing these services to run simultaneously on HTTP/1 and HTTP/2. The Dubbo TypeScript SDK supports defining services using IDL or language-specific approaches and provides a lightweight API to publish or invoke these services.
Dubbo-js has officially released its first alpha version supporting the Dubbo3 protocol in September, which promises to transform the architecture and communication models between front-end and back-end of microservices, enabling direct access to back-end Dubbo RPC services from browser pages or web servers. The project is rapidly evolving, and developers interested in participating in the apache/dubbo-js project are welcome to search for the DingTalk group: 29775027779 to join the developer group.
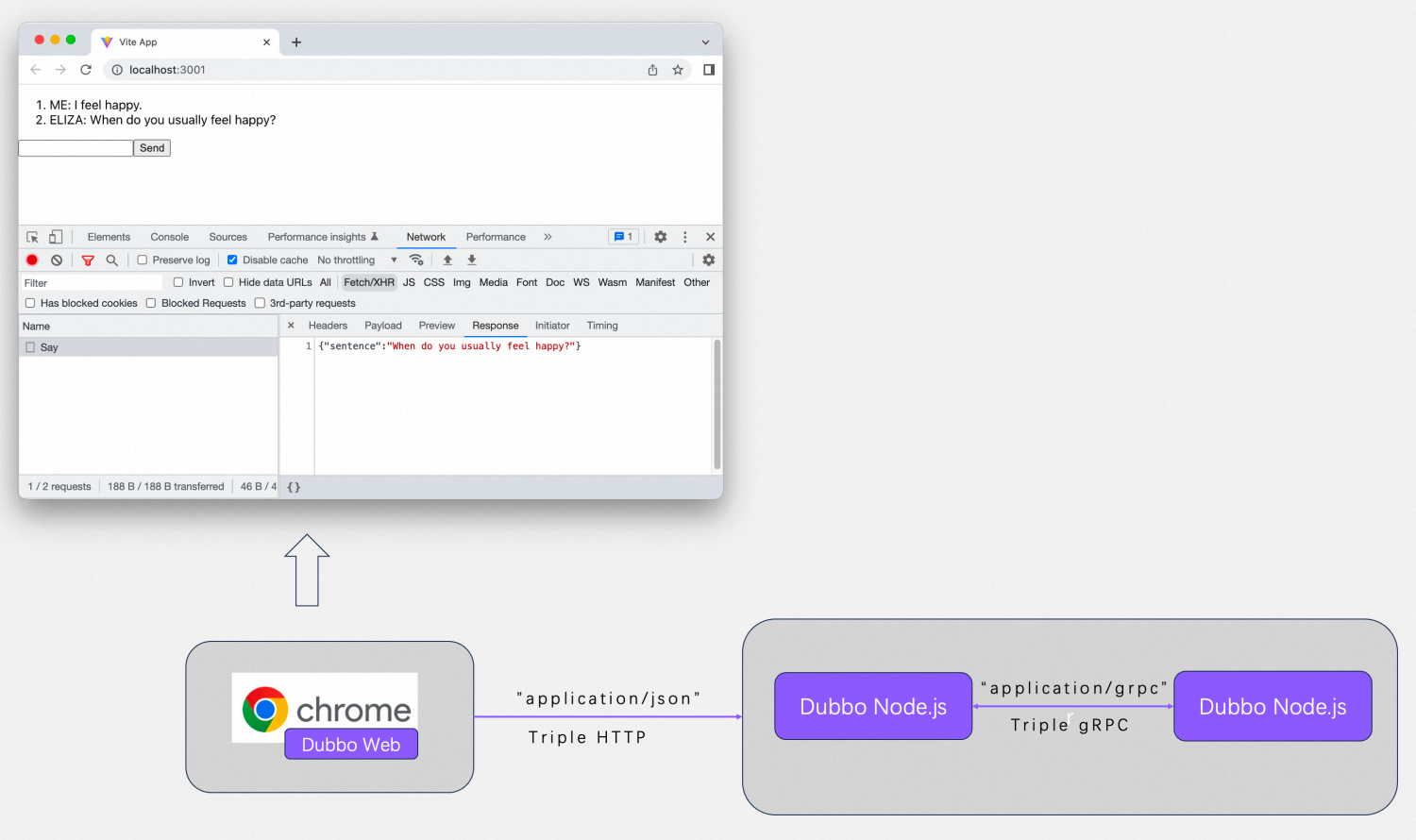
Browser Web Application Example
This example demonstrates how to develop a web application running in the browser using dubbo-js, where the web page calls back-end services developed in dubbo node.js to generate page content. This example showcases both IDL and non-IDL coding modes.
IDL Mode
Prerequisites
First, we will use Vite to generate our front-end project template, which includes all the necessary feature support we’ll need later.
npm create vite@latest -- dubbo-web-example --template react-ts
cd dubbo-web-example
npm install
Due to using Protocol Buffer, we first need to install the relevant code generation tools, including @bufbuild/protoc-gen-es, @bufbuild/protobuf, @apachedubbo/protoc-gen-apache-dubbo-es, and @apachedubbo/dubbo.
npm install @bufbuild/protoc-gen-es @bufbuild/protobuf @apachedubbo/protoc-gen-apache-dubbo-es @apachedubbo/dubbo
Define Services Using Proto
Now, define a Dubbo service using Protocol Buffer (IDL).
Create the util/proto directory under src and generate the file
mkdir -p src/util/proto && touch src/util/proto/example.proto
Write the content
syntax = "proto3";
package apache.dubbo.demo.example.v1;
message SayRequest {
string sentence = 1;
}
message SayResponse {
string sentence = 1;
}
service ExampleService {
rpc Say(SayRequest) returns (SayResponse) {}
}
This file declares a service called ExampleService, defining the Say method along with its request parameter SayRequest and return value SayResponse.
Generate Code
Create a gen directory as the target directory for generated files
mkdir -p src/util/gen
Run the following command to generate the code files in the gen directory using plugins like protoc-gen-es, protoc-gen-apache-dubbo-es
PATH=$PATH:$(pwd)/node_modules/.bin \
protoc -I src/util/proto \
--es_out src/util/gen \
--es_opt target=ts \
--apache-dubbo-es_out src/util/gen \
--apache-dubbo-es_opt target=ts \
example.proto
After running the command, you should see the following generated files in the target directory:
├── src
│ ├── util
│ │ ├── gen
│ │ │ ├── example_dubbo.ts
│ │ │ └── example_pb.ts
│ │ └── proto
│ │ └── example.proto
Create App
First, install @apachedubbo/dubbo-web
npm install @apachedubbo/dubbo-web
Now we can import the service from the package and set up a client. Add the following content in App.tsx:
import { useState } from "react";
import "./App.css";
import { createPromiseClient } from "@apachedubbo/dubbo";
import { createDubboTransport } from "@apachedubbo/dubbo-web";
// Import service definition that you want to connect to.
import { ExampleService } from "./util/gen/example_dubbo";
// The transport defines what type of endpoint we're hitting.
// In our example we'll be communicating with a Dubbo endpoint.
const transport = createDubboTransport({
baseUrl: "http://localhost:8080",
});
// Here we make the client itself, combining the service
// definition with the transport.
const client = createPromiseClient(ExampleService, transport, { serviceGroup: 'dubbo', serviceVersion: '1.0.0' });
function App() {
const [inputValue, setInputValue] = useState("");
const [messages, setMessages] = useState<
{
fromMe: boolean;
message: string;
}[]
>([]);
return (
<>
<ol>
{messages.map((msg, index) => (
<li key={index}>{`${msg.fromMe ? "ME:" : "Dubbo Server:"} ${msg.message}`}</li>
))}
</ol>
<form
onSubmit={async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
// Clear inputValue since the user has submitted.
setInputValue("");
// Store the inputValue in the chain of messages and
// mark this message as coming from "me"
setMessages((prev) => [
...prev,
{
fromMe: true,
message: inputValue,
},
]);
const response = await client.say({
sentence: inputValue,
});
setMessages((prev) => [
...prev,
{
fromMe: false,
message: response.sentence,
},
]);
}}
>
<input value={inputValue} onChange={(e) => setInputValue(e.target.value)} />
<button type="submit">Send</button>
</form>
</>
);
}
export default App;
Run the following command to obtain the sample page
npm run dev
Start Server
Next, we need to start the server. You can develop the server in any language supported by Dubbo, such as Java, Go, or Node.js. Here we will use a Node.js server embedded with Dubbo services, detailed in the Node.js Development of Dubbo Backend Services guide.
However, we need to make an additional modification to the Node.js example: import @fastify/cors to solve the CORS issue for front-end requests.
npm install @fastify/cors
The modification in the server.ts file should include
...
import cors from "@fastify/cors";
...
async function main() {
const server = fastify();
...
await server.register(cors, {
origin: true,
});
...
await server.listen({ host: "localhost", port: 8080 });
...
}
void main();
Finally, run the code to start the service
npx tsx server.ts
Non-IDL Mode
In upcoming versions, we will continue to provide non-IDL mode communication support for easier access to non-IDL back-end services. Here, we will quickly look at the use of non-IDL mode.
Again, first install @apachedubbo/dubbo, @apachedubbo/dubbo-web
npm install @apachedubbo/dubbo @apachedubbo/dubbo-web
Now you can start a client and initiate a call. The code in App.tsx is mostly identical to the IDL mode, with the following differences:
// ...
// set backend server to connect
const transport = createDubboTransport({
baseUrl: "http://localhost:8080",
});
// init client
const client = createPromiseClient(transport);
function App() {
// ...
// call remote Dubbo service
const response = await client.call(
"apache.dubbo.demo.example.v1.ExampleService",
"say",
{
sentence: inputValue,
});
}
Run the following command to get the sample page
npm run dev
Summary
Access back-end Dubbo RPC services directly from browser pages or web servers! The upgrade of the Dubbo Triple protocol and the release of the Dubbo JavaScript SDK provide a significant enhancement to the entire microservices ecosystem, expecting to see it change the entire microservices architecture and front-end and back-end communication patterns in the future.
Dubbo-js has just released the first alpha version supporting the Dubbo3 Triple protocol in September, and the project is rapidly evolving. Developers interested in participating in the apache/dubbo-js project are welcome to join the organization through the following methods:
- Search for DingTalk group: 29775027779 to join the developer group.
- Follow the public account
apachedubbo, reply “dubbojs” to accept the invitation to join the development team.