This article is more than one year old. Older articles may contain outdated content. Check that the information in the page has not become incorrect since its publication.
A Quick Guide to Understanding the Core Capabilities of Dubbo
Introduction to Dubbo
One-Sentence Definition
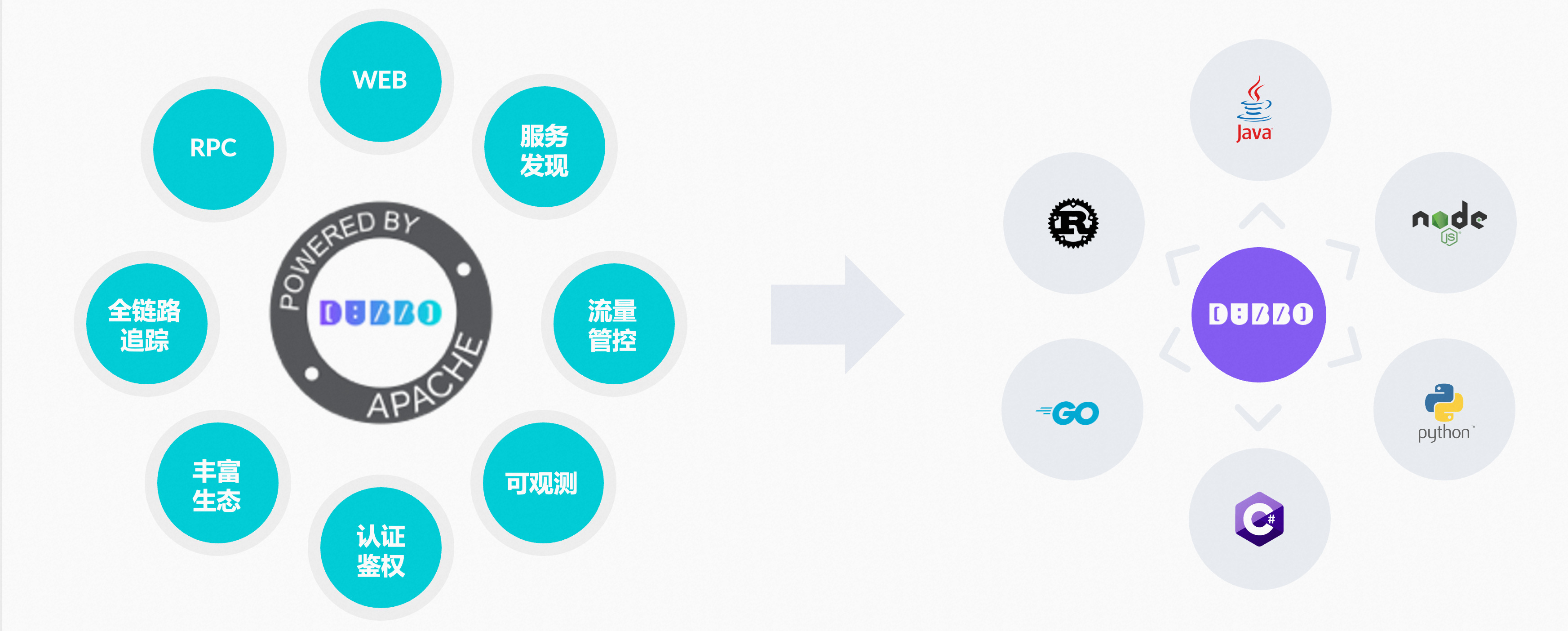
Apache Dubbo is a microservices development framework that helps solve communication problems in microservices development while providing service governance capabilities for building enterprise-level microservices. Dubbo is not tied to a specific programming language; our goal is to provide a peer-to-peer microservices development experience for all mainstream languages.
Basic Architecture
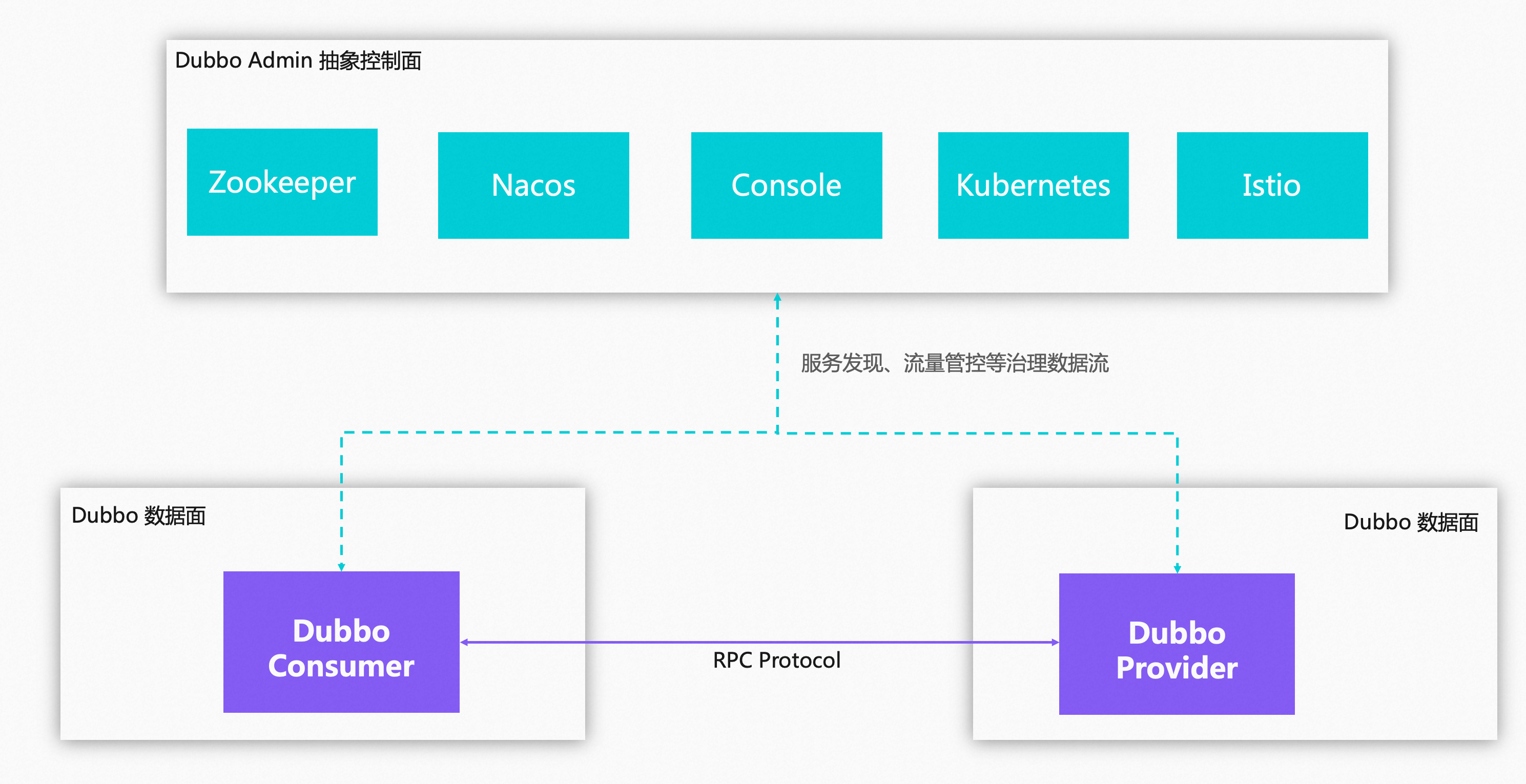
Dubbo’s architecture is divided into the data plane and control plane. In the data plane, microservices developed with Dubbo communicate via the RPC protocol. The DubboAdmin control plane serves as an abstract entry point for service governance, composed of a series of optional service governance components responsible for service discovery, traffic control policies, and visual monitoring of Dubbo clusters.
Industry Applications
Dubbo was designed to address the challenges of large-scale microservices cluster practices within Alibaba and is currently widely used in microservices practices across almost all industries.
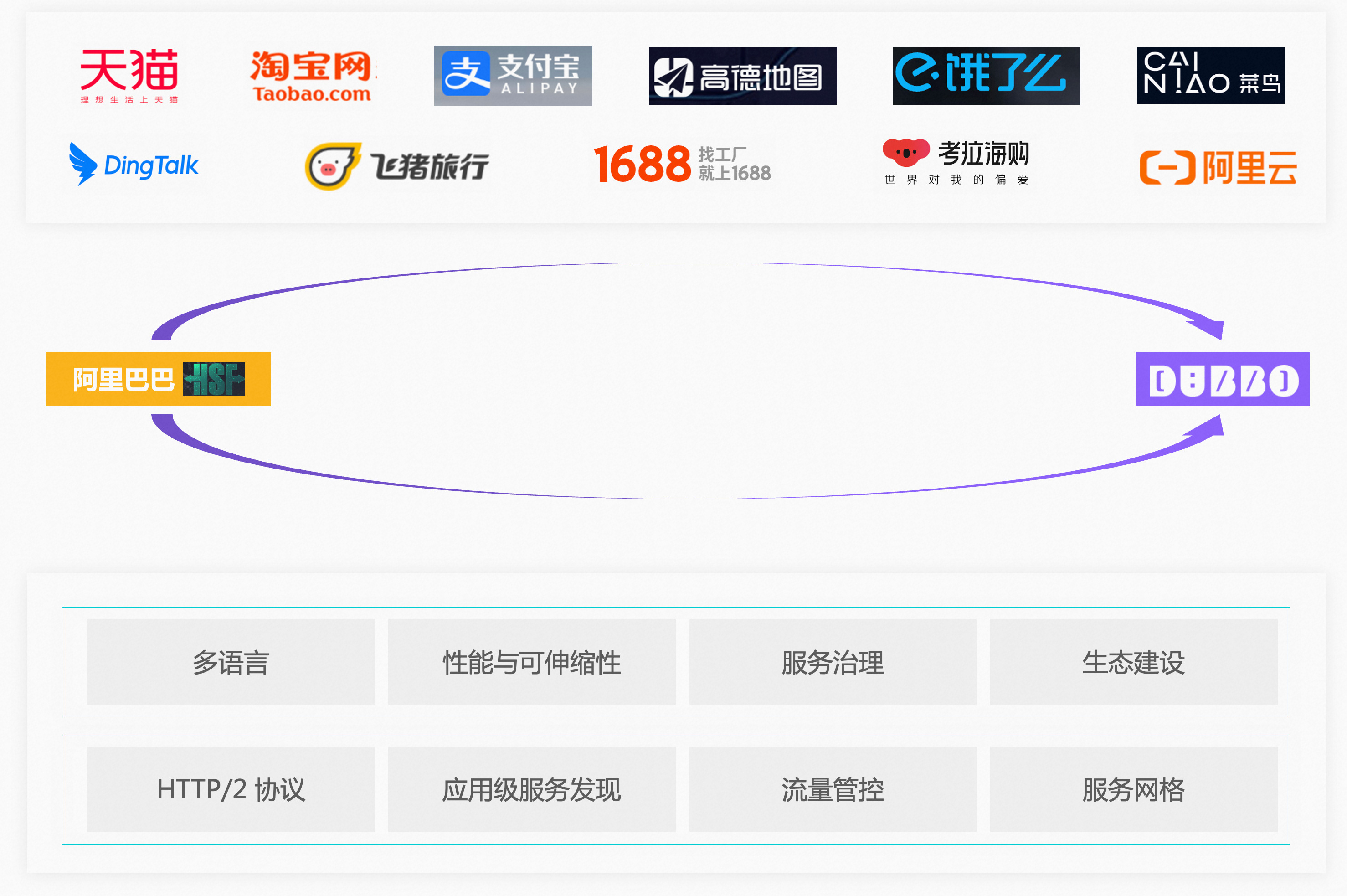
For instance, in 2021, Alibaba built the next-generation microservices framework Dubbo3, based on years of internal HSF framework practice, targeting cloud-native architecture to solve issues related to performance, governance upgrades, service mesh, and more. As of now, Alibaba has fully completed the migration from HSF to Dubbo3, with core businesses running on open-source Dubbo3.
What Core Capabilities Does Dubbo Provide?
Provides Microservices Abstraction and Framework
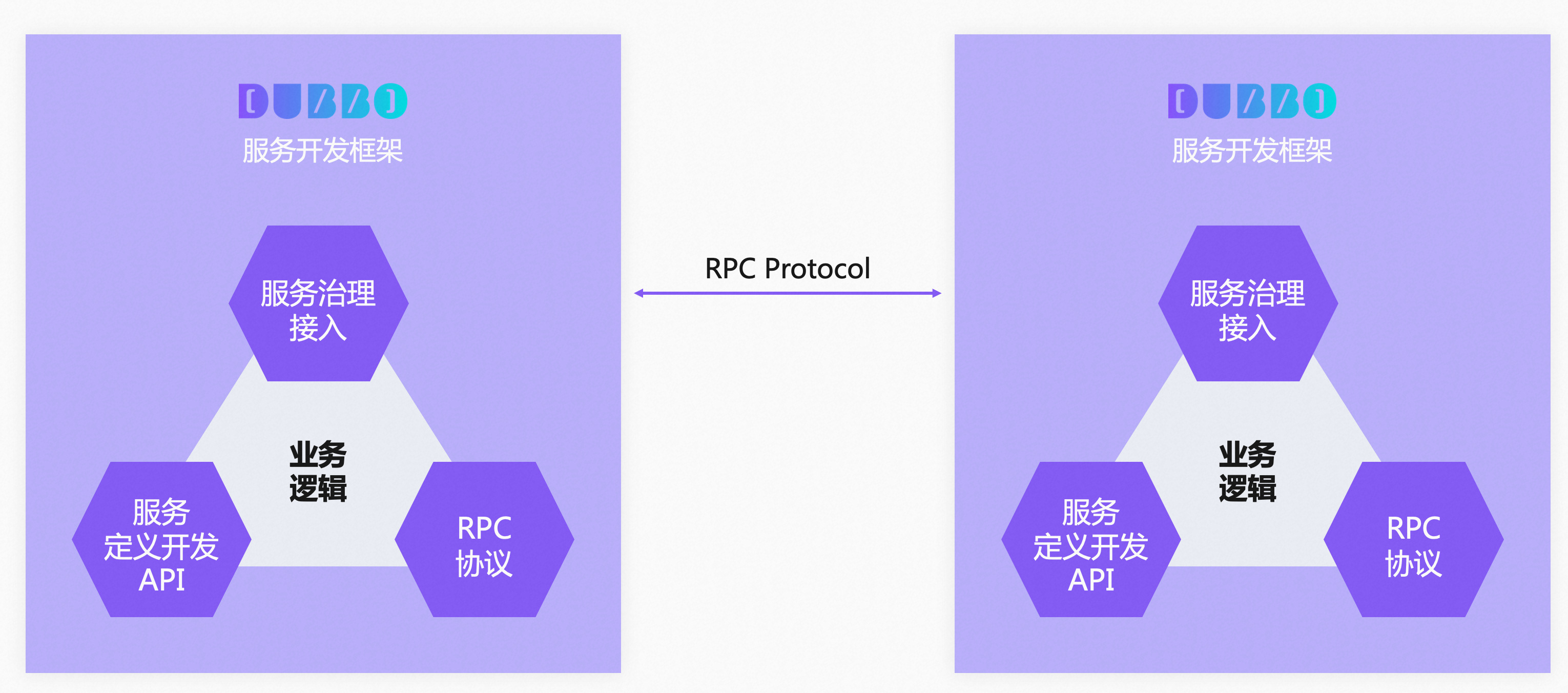
Firstly, Dubbo solves the issues of microservice definition, exposure, communication, and governance in business applications as a service development framework, defining a set of microservices programming paradigms for business application development. Specifically, Dubbo provides three core capabilities for business applications: microservices development API, RPC protocol, and service governance, allowing developers to truly focus on business logic development.
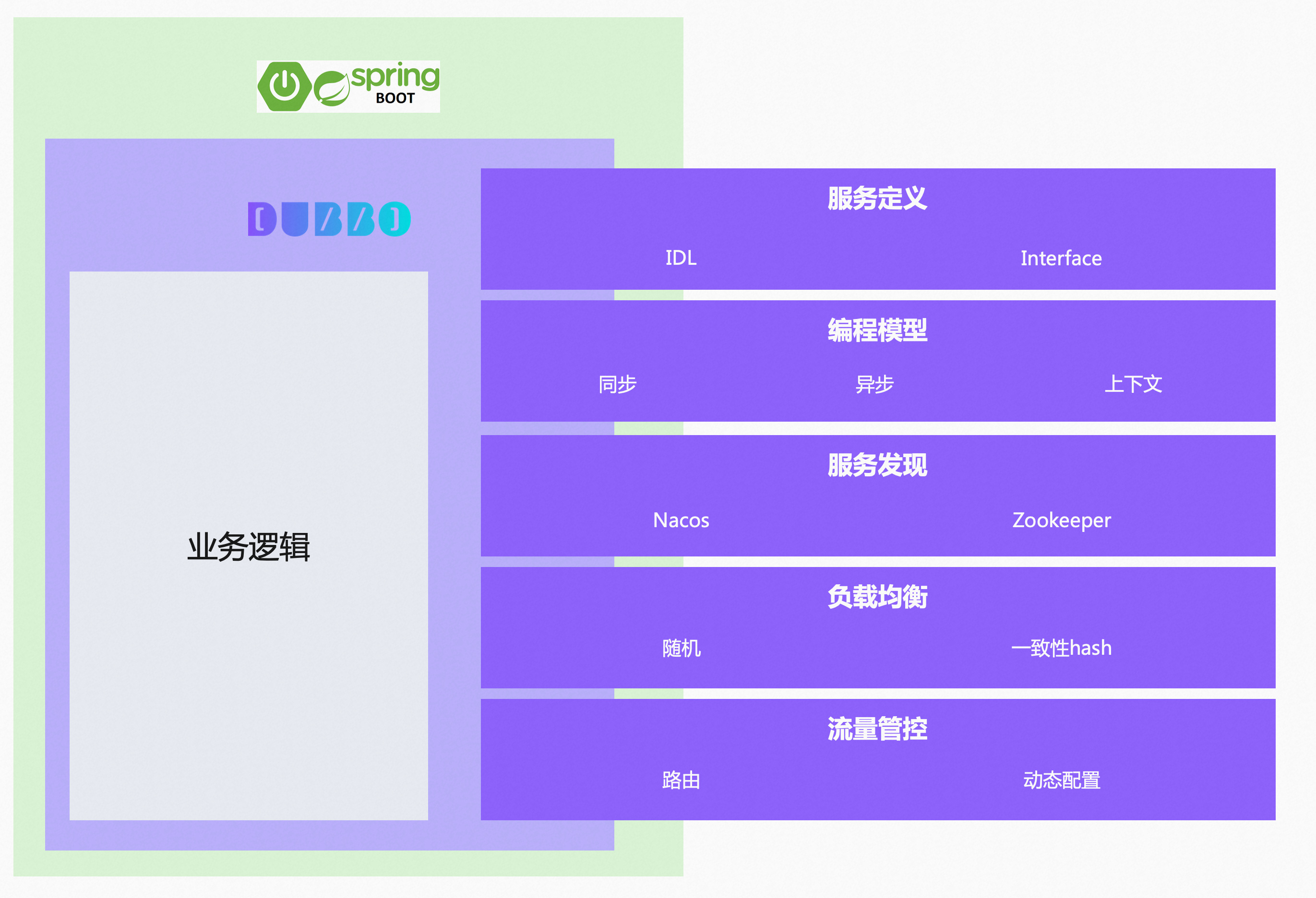
Dubbo is not a replacement for application frameworks; it works well on top of mainstream programming frameworks in every language. For example, Dubbo can integrate well with Spring in Java, providing capabilities like service definition, microservices programming, service discovery, load balancing, and traffic control.
Provides Flexible Communication Protocol Switching Capability
In terms of communication, Dubbo differs from other RPC frameworks in that it is not tied to a specific protocol; you can choose any communication protocol at the bottom level, such as HTTP/2, TCP, gRPC, REST, Hessian, etc., while enjoying a unified API and equal service governance capabilities.
Everything is Expandable
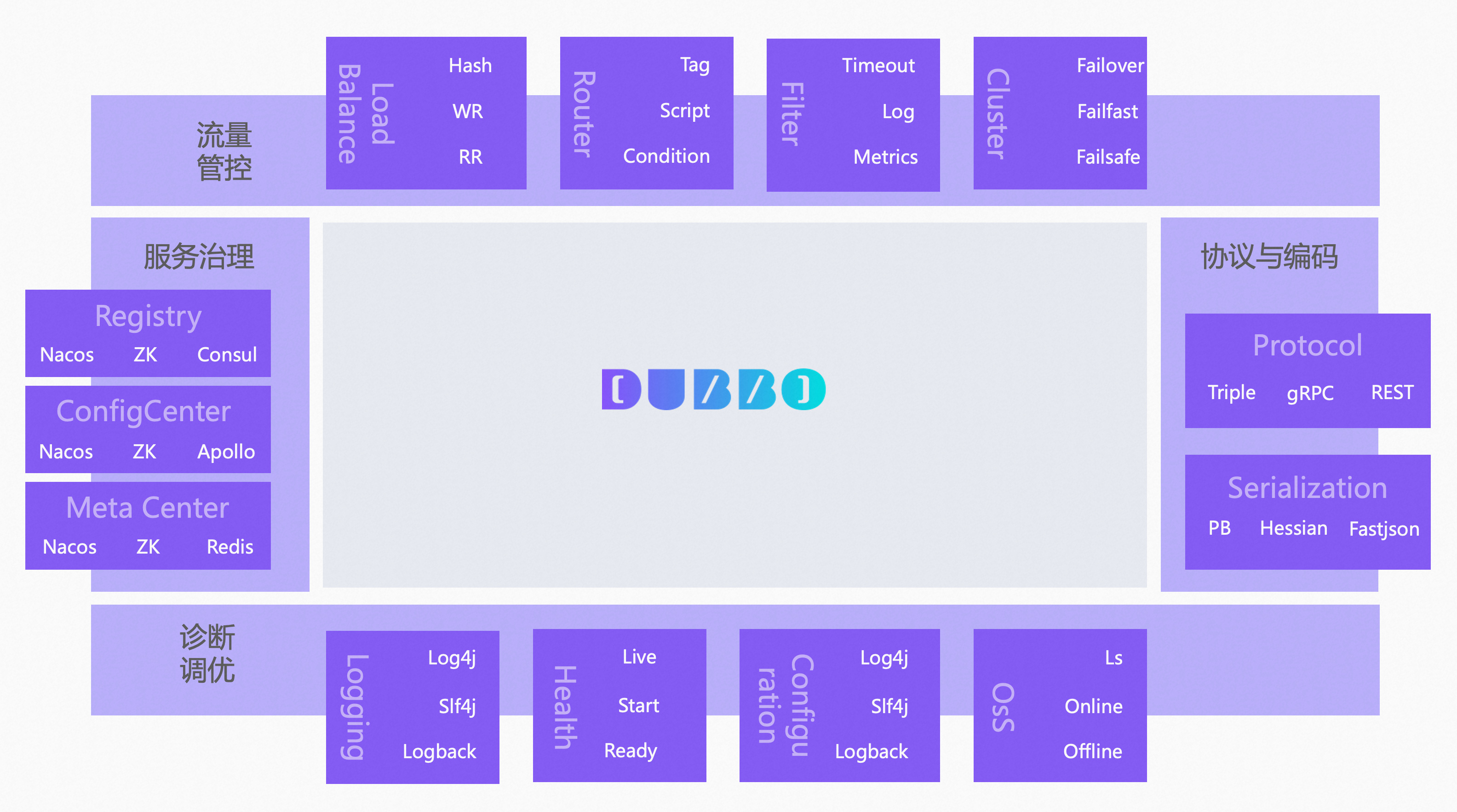
Another advantage of Dubbo lies in its extensibility design. You can expand in areas such as traffic control, protocol encoding, diagnostic tuning, and service governance to meet all demands for enterprise-level microservices development and operations.
Rich Ecosystem
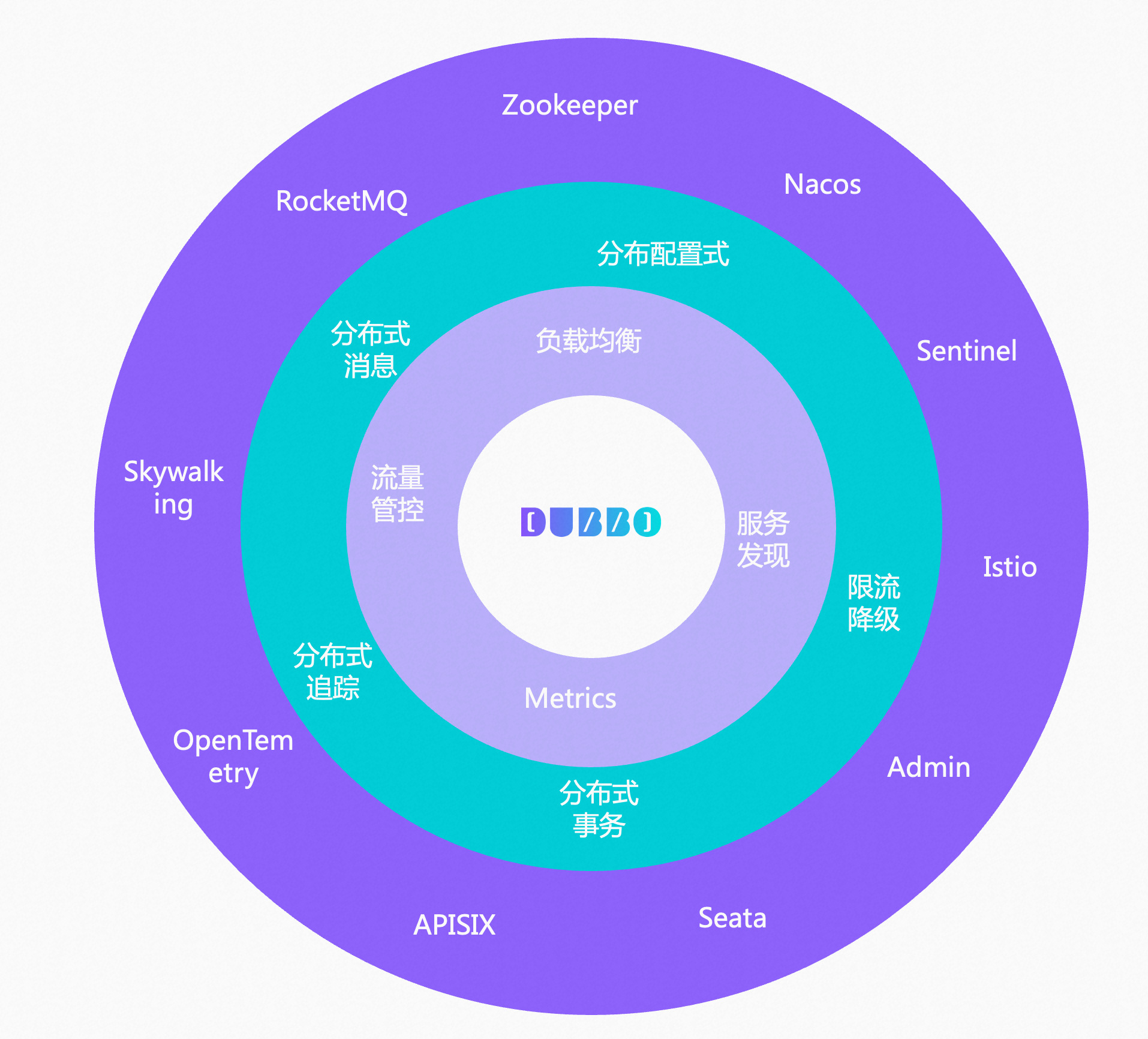
Based on extensibility, Dubbo officially provides a rich ecosystem integration covering all mainstream open-source microservices components.
Service Mesh
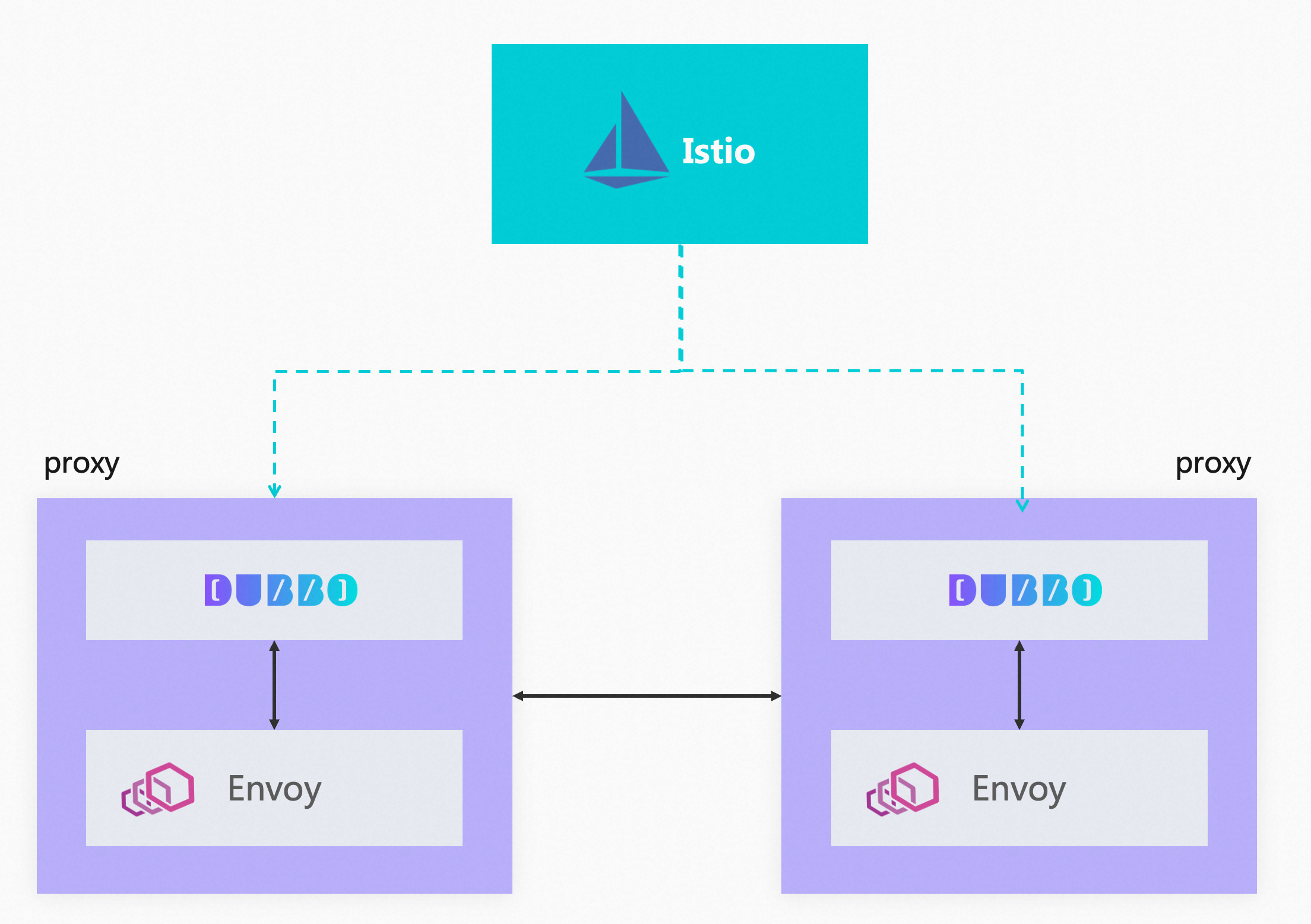
For service mesh architectures, Dubbo can also easily integrate with native Istio systems; it supports data planes with both Envoy-deployed Proxy modes and Proxyless modes without Envoy, providing more flexible data plane options.
How Simple is it to Build Enterprise-Level Dubbo Microservices? You Just Need 4 Steps
We take Java microservices development as an example.
Step 1
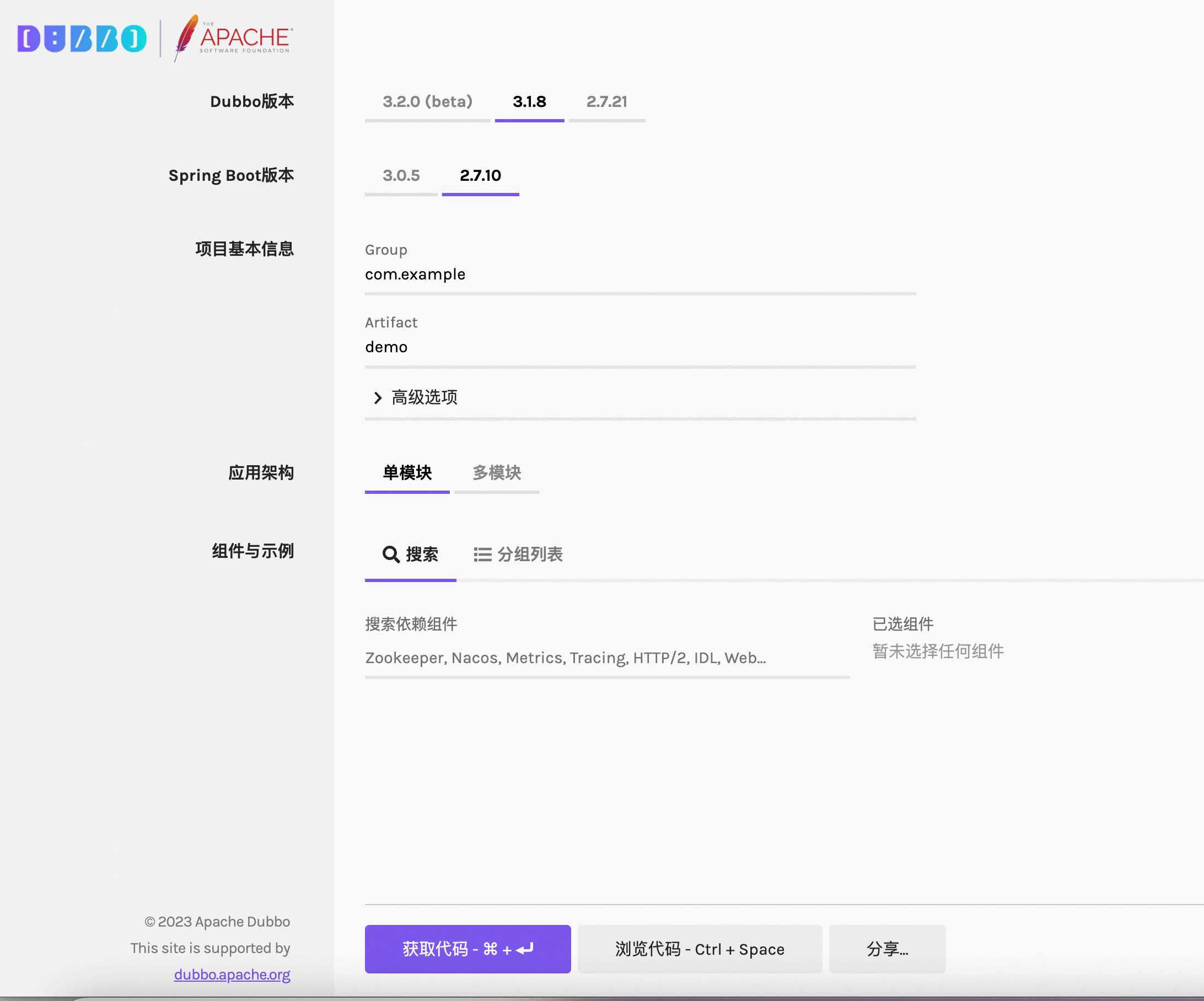
Use the official scaffolding to quickly create project templates by simply choosing the dependency versions and components, and clicking “Get Code”.
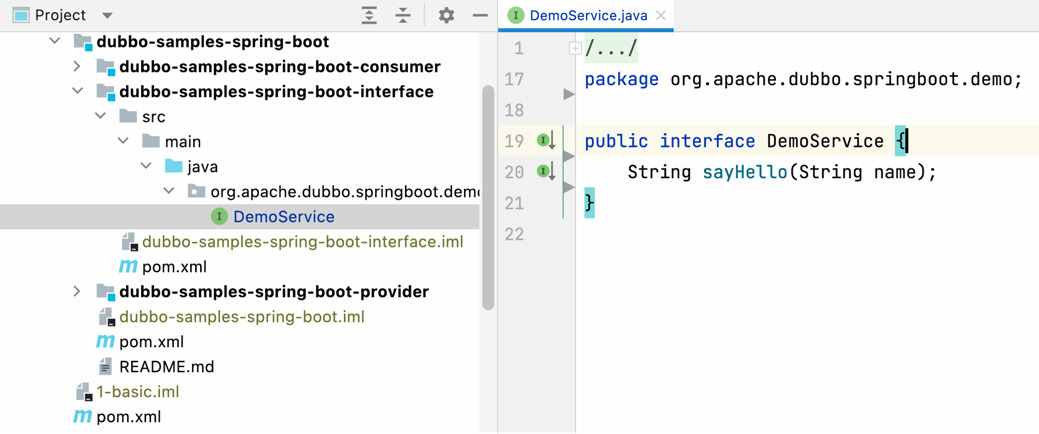
Step 2
Import the template project into your IDE development environment.
Define a Java interface as a Dubbo service.
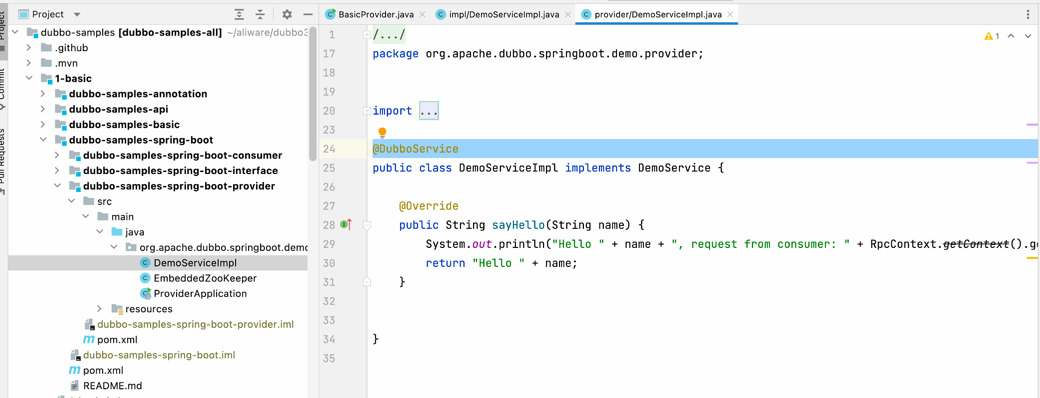
Develop the Dubbo server, implement the interface, and complete business logic coding. Publish the service through a simple annotation configuration.
Develop the Dubbo client, declare the Dubbo service with annotations, and initiate remote method calls. At this point, the development work is complete.
Step 3
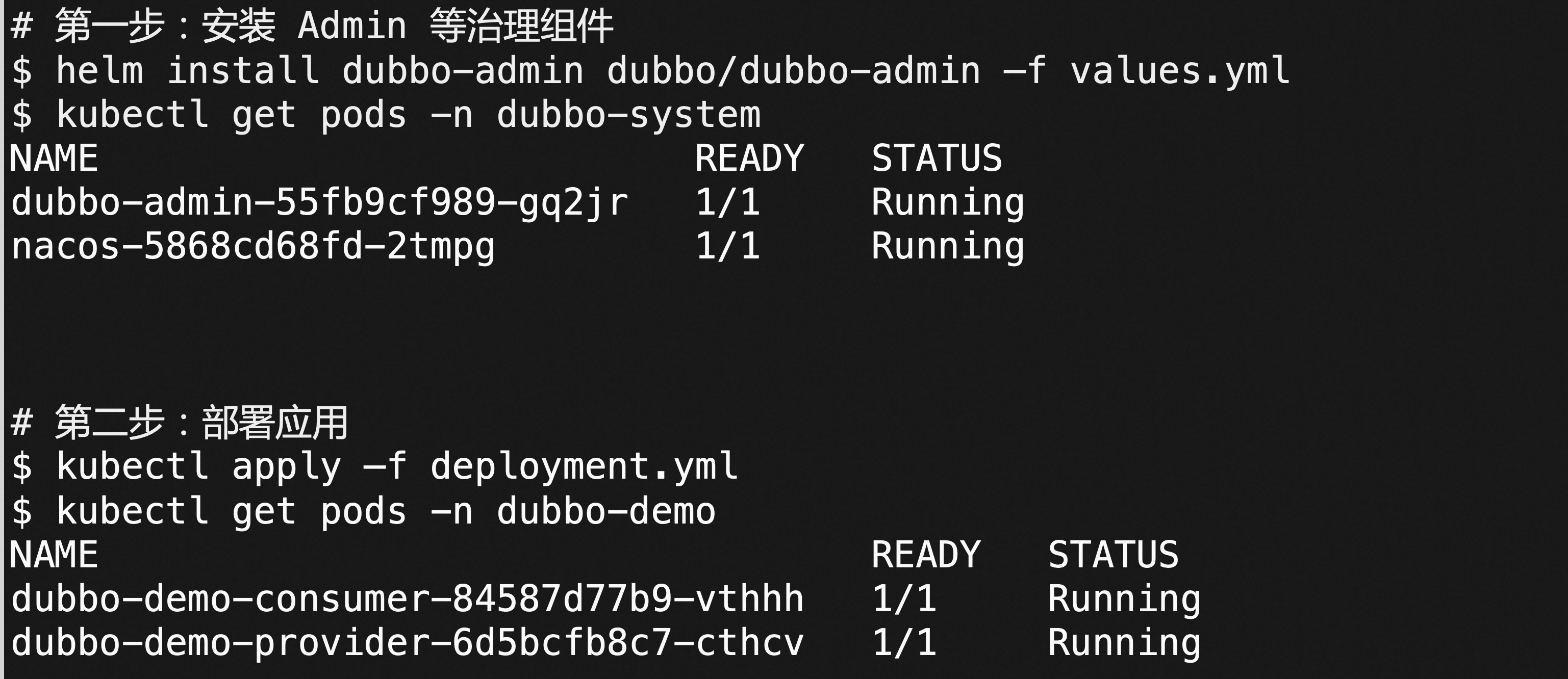
Enter the deployment phase; we choose Kubernetes as the deployment environment.
First, install Dubbo Admin and other service governance components with a single command. After successful installation, check the deployment status. Next, start deploying the business applications and confirm until the application starts normally.
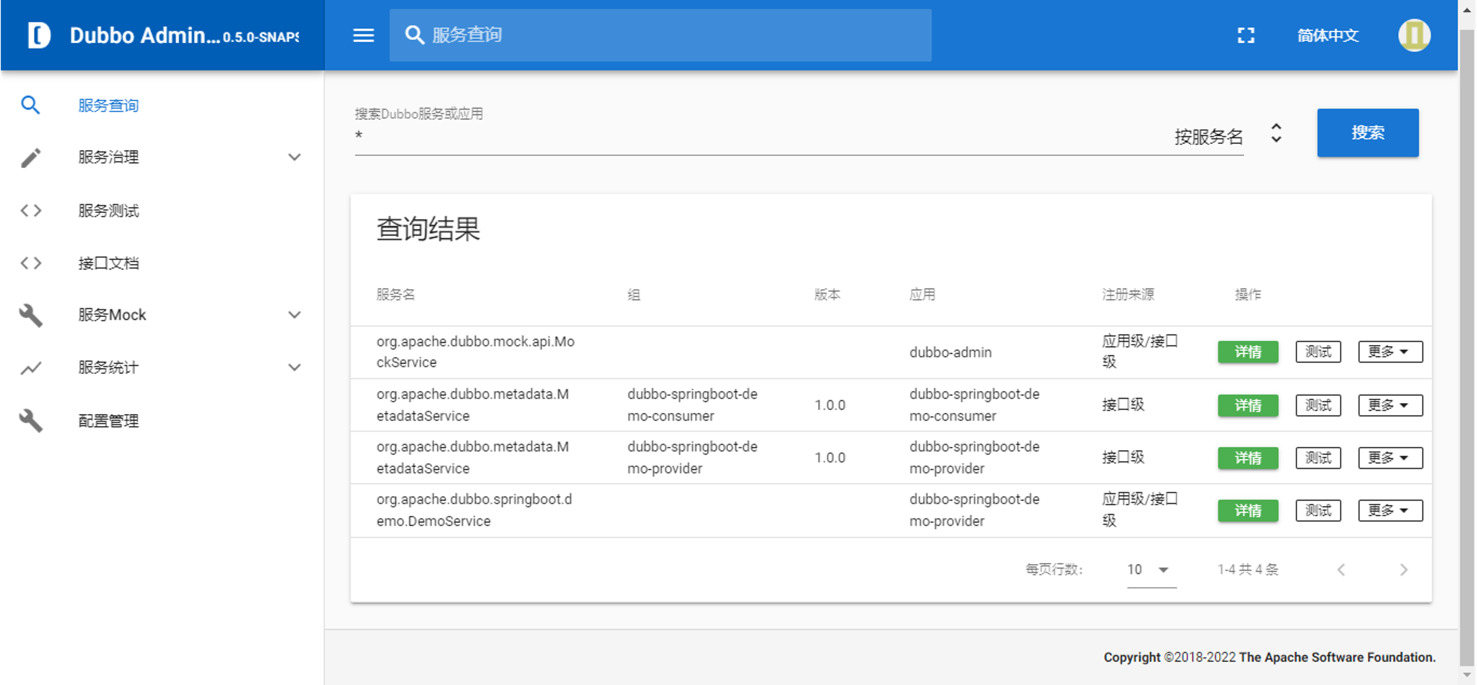
Then, we can open the Admin console to check the service deployment and invocation statistics. Here is the display effect of the Dubbo Admin console page, showing the deployment status of the just-started Dubbo service; in addition, Admin provides more detailed traffic monitoring. Clicking on Service Statistics leads to the monitoring page.
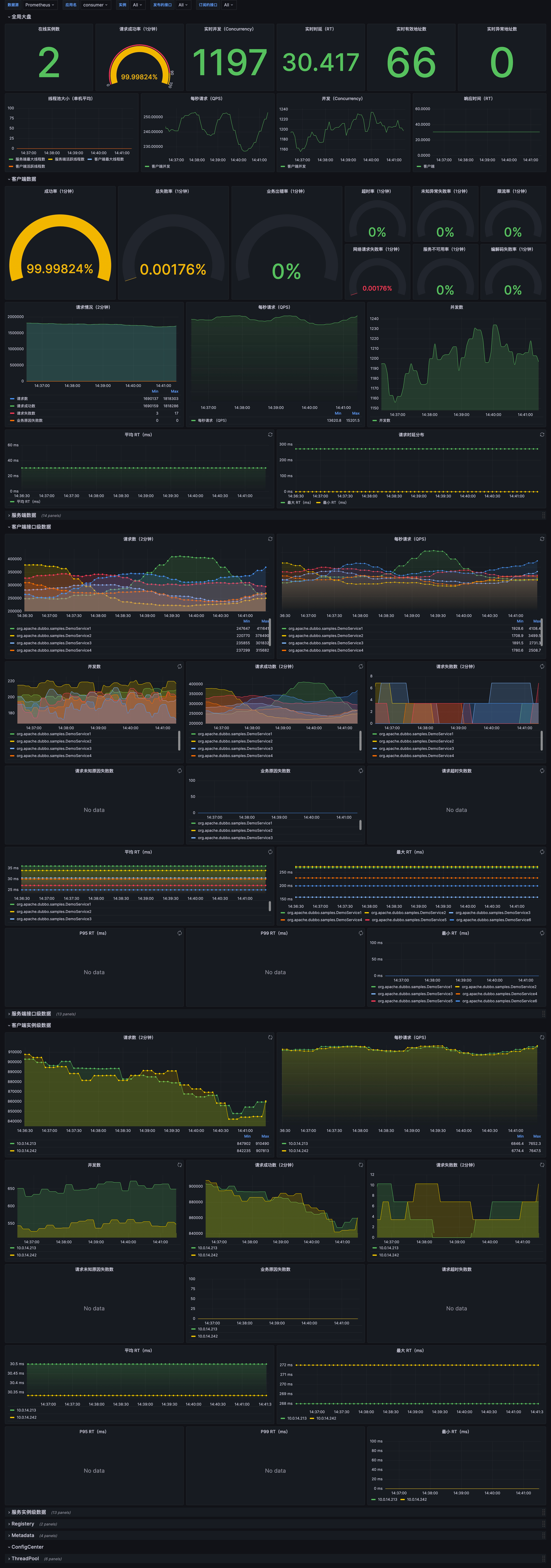
You can learn about the detailed operational status of the Dubbo cluster, including each application’s external services and invocation services, QpS, success rates, and check the resource health status of each instance.
Step 4
Perform traffic control. Once the application is running smoothly, further control the traffic access behavior, including implementing canary releases, full-link gray release, dynamically adjusting timeout settings, adjusting weights, proportionate traffic distribution, and parameter routing. The console provides a visual entry point for traffic governance rule operations, where traffic rules can be directly issued.
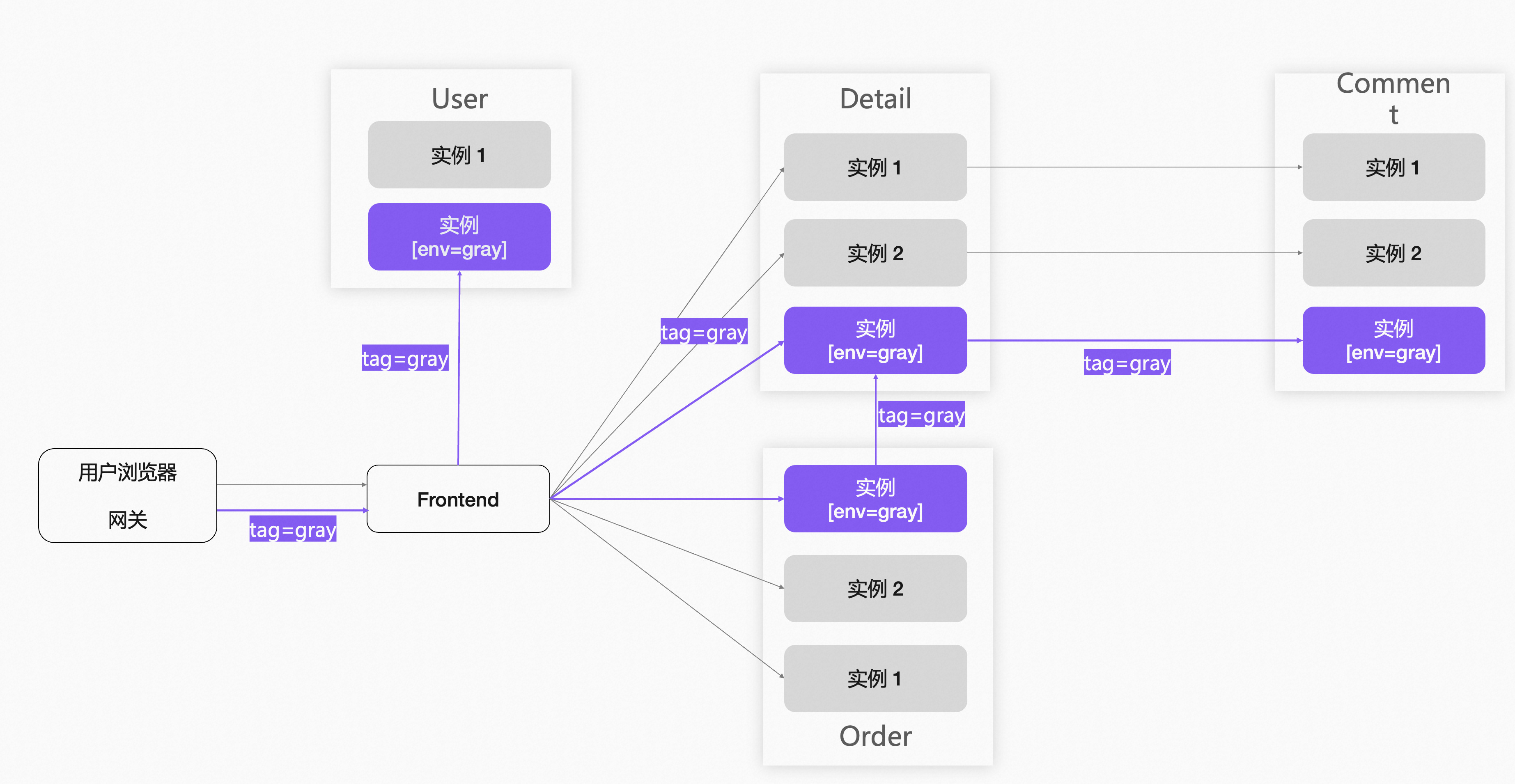
For example, in a gray isolation scenario in an online environment, through Dubbo’s traffic control mechanism, we can label a portion of machines for each application with a gray tag. For incoming traffic labeled as gray, we can control it to ensure it only circulates within Dubbo instances marked as gray, achieving full-link logical isolation, which is very useful for isolating multiple development environments and online gray testing.
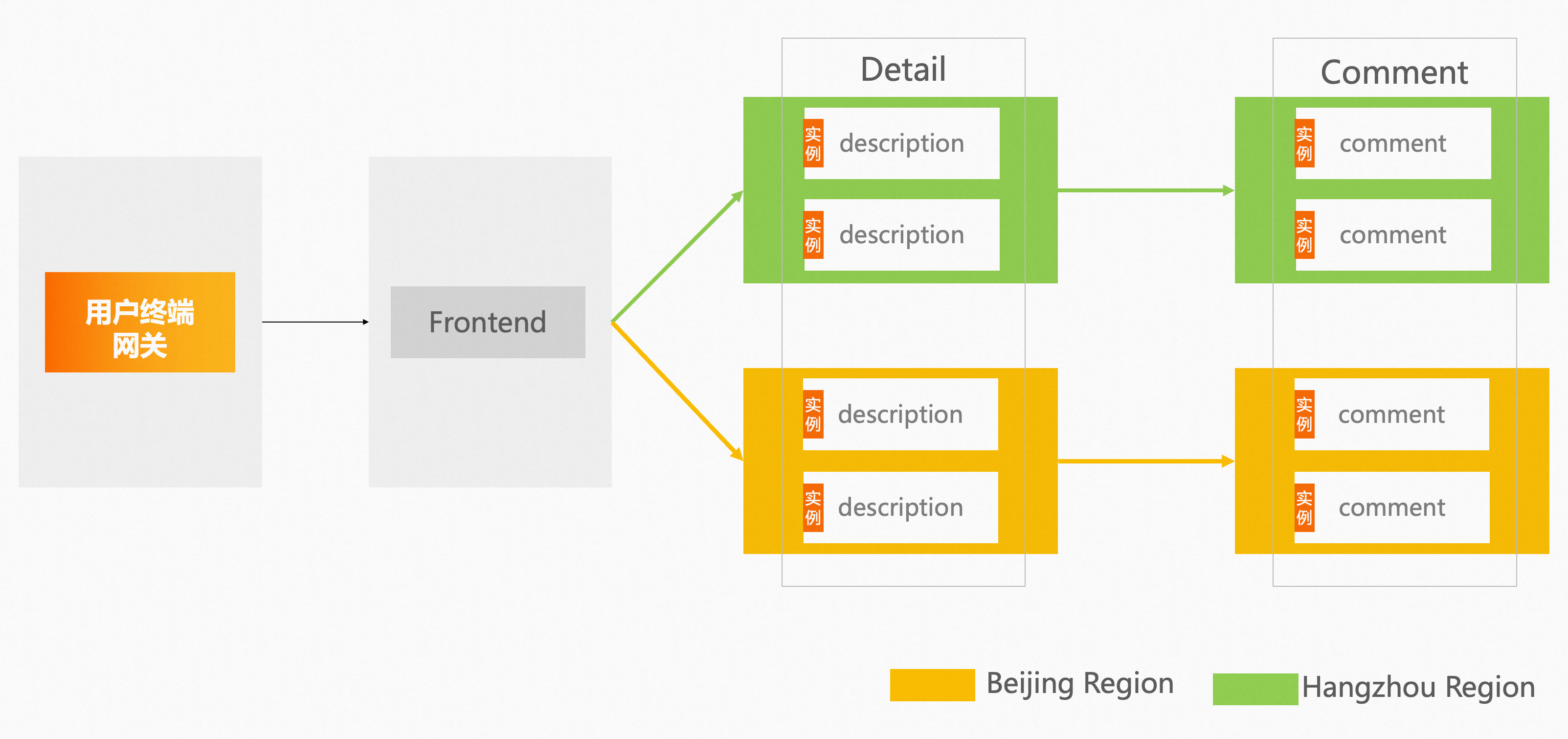
In scenarios where priority calls are made to the same region, there are two applications deployed in multiple regions. The purple represents the Hangzhou region, and the blue represents the Beijing region; applications deployed in the orange area will prefer to access applications in the same region to reduce access latency, and the services deployed in the blue region will operate similarly.
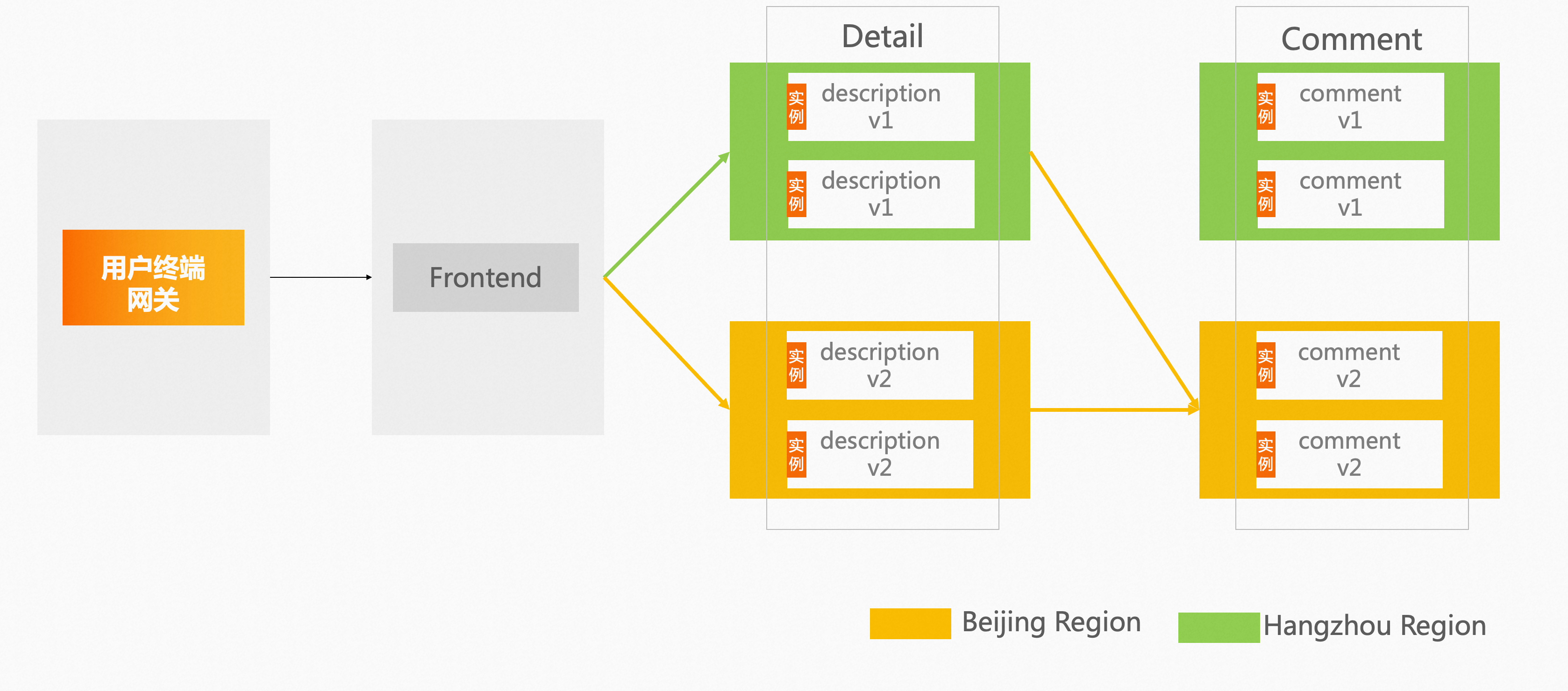
When instances deployed in the same region are unavailable, calls will automatically switch to other available regions, ensuring overall availability.
Conclusion
Now, please start your Dubbo journey.