This article is more than one year old. Older articles may contain outdated content. Check that the information in the page has not become incorrect since its publication.
How to use Seata to ensure consistency between Dubbo Microservices
This article will introduce you how to use Seata to ensure consistency between Dubbo Microservices.
Use case
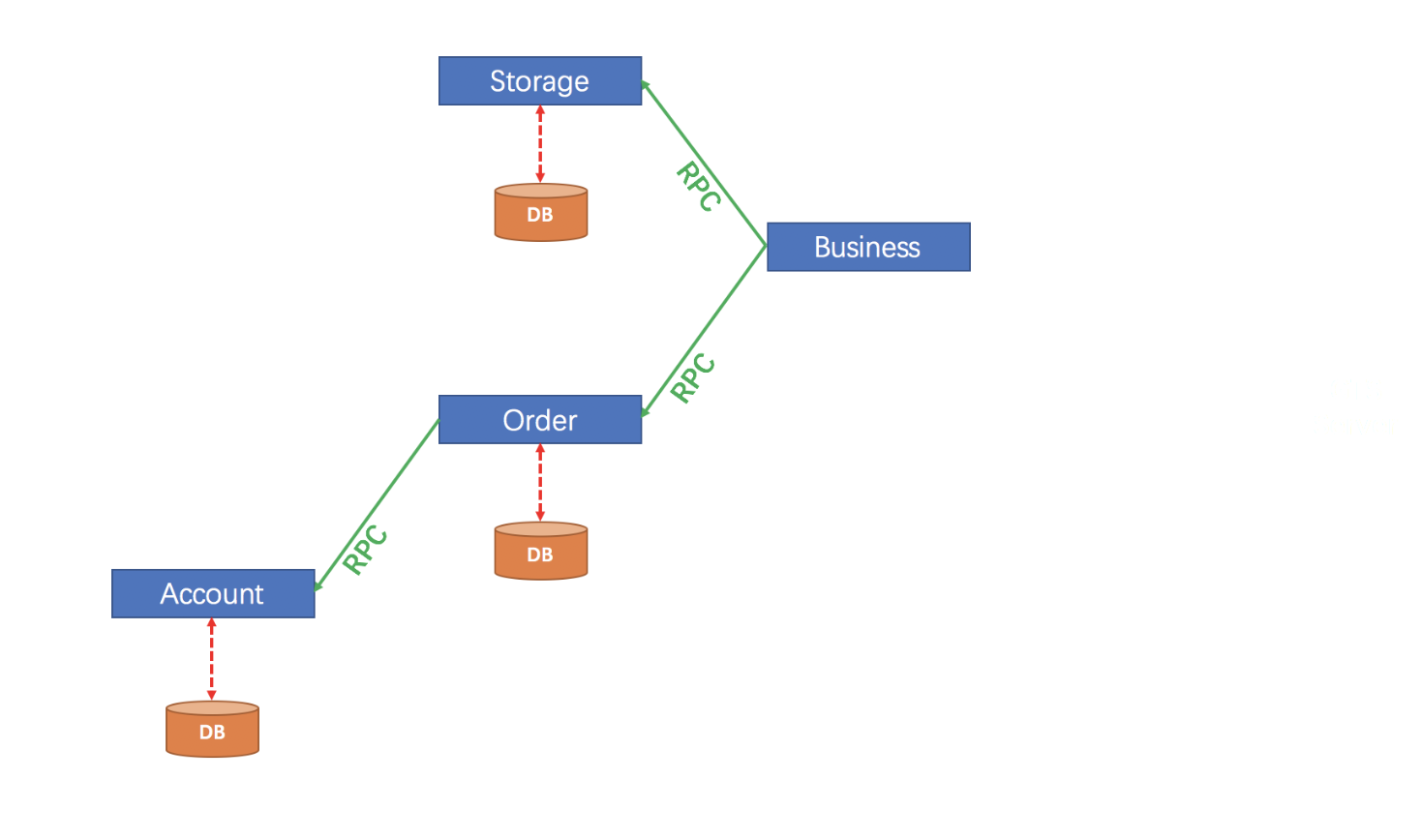
A business logic for user purchasing commodities. The whole business logic is powered by 3 microservices:
- Storage service: deduct storage count on given commodity.
- Order service: create order according to purchase request.
- Account service: debit the balance of user’s account.
Architecture
StorageService
public interface StorageService {
/**
* deduct storage count
*/
void deduct(String commodityCode, int count);
}
OrderService
public interface OrderService {
/**
* create order
*/
Order create(String userId, String commodityCode, int orderCount);
}
AccountService
public interface AccountService {
/**
* debit balance of user's account
*/
void debit(String userId, int money);
}
Main business logic
public class BusinessServiceImpl implements BusinessService {
private StorageService storageService;
private OrderService orderService;
/**
* purchase
*/
public void purchase(String userId, String commodityCode, int orderCount) {
storageService.deduct(commodityCode, orderCount);
orderService.create(userId, commodityCode, orderCount);
}
}
public class StorageServiceImpl implements StorageService {
private StorageDAO storageDAO;
@Override
public void deduct(String commodityCode, int count) {
Storage storage = new Storage();
storage.setCount(count);
storage.setCommodityCode(commodityCode);
storageDAO.update(storage);
}
}
public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService {
private OrderDAO orderDAO;
private AccountService accountService;
public Order create(String userId, String commodityCode, int orderCount) {
int orderMoney = calculate(commodityCode, orderCount);
accountService.debit(userId, orderMoney);
Order order = new Order();
order.userId = userId;
order.commodityCode = commodityCode;
order.count = orderCount;
order.money = orderMoney;
return orderDAO.insert(order);
}
}
Distributed Transaction Solution with Seata
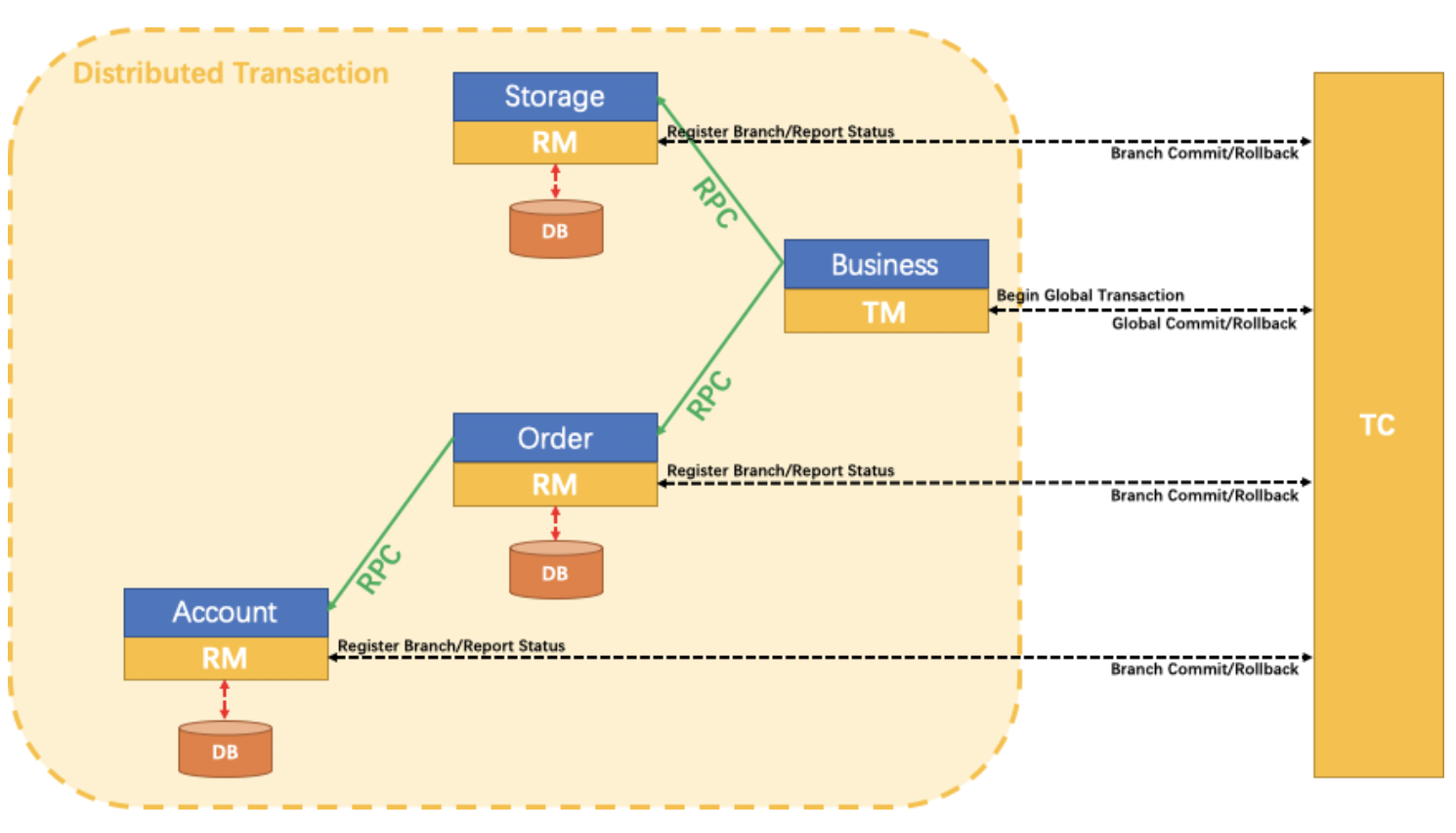
We just need an annotation @GlobalTransactional on business method:
@GlobalTransactional
public void purchase(String userId, String commodityCode, int orderCount) {
......
}
Example powered by Dubbo + Seata
Step 1: Setup database
- Requirement: MySQL with InnoDB engine.
Note: In fact, there should be 3 database for the 3 services in the example use case. However, we can just create one database and configure 3 data sources for simple.
Modify Spring XML with the database URL/username/password you just created.
dubbo-account-service.xml dubbo-order-service.xml dubbo-storage-service.xml
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://x.x.x.x:3306/xxx" />
<property name="username" value="xxx" />
<property name="password" value="xxx" />
Step 2: Create undo_log table for Seata
UNDO_LOG table is required by Seata AT mode.
-- Note that when Seata version is upgraded to 0.3.0+, it is changed from the previous normal index to the unique index.
CREATE TABLE `undo_log` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`branch_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL,
`xid` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`context` varchar(128) NOT NULL,
`rollback_info` longblob NOT NULL,
`log_status` int(11) NOT NULL,
`log_created` datetime NOT NULL,
`log_modified` datetime NOT NULL,
`ext` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `ux_undo_log` (`xid`,`branch_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
Step 3: Create tables for example business
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `storage_tbl`;
CREATE TABLE `storage_tbl` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`commodity_code` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`count` int(11) DEFAULT 0,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY (`commodity_code`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `order_tbl`;
CREATE TABLE `order_tbl` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_id` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`commodity_code` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`count` int(11) DEFAULT 0,
`money` int(11) DEFAULT 0,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `account_tbl`;
CREATE TABLE `account_tbl` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_id` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`money` int(11) DEFAULT 0,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
Step 4: Start Seata-Server
- Download server package, unzip it.
- Start Seata-Server
Usage: sh seata-server.sh(for linux and mac) or cmd seata-server.bat(for windows) [options]
Options:
--host, -h
The host to bind.
Default: 0.0.0.0
--port, -p
The port to listen.
Default: 8091
--storeMode, -m
log store mode : file、db
Default: file
--help
e.g.
sh seata-server.sh -p 8091 -h 127.0.0.1 -m file
Step 5: Run example
- Start AccountService (DubboAccountServiceStarter).
- Start StockService (DubboStorageServiceStarter).
- Start OrderService (DubboOrderServiceStarter).
- Run BusinessService for test (DubboBusinessTester).
Related projects
- Seata: https://github.com/seata/seata
- Seata Samples : https://github.com/seata/seata-samples